The most commonly used remedies for bursitis, which is the inflammation of the fluid pocket that cushions the friction between the tendons and bones or skin, in the joint, are mainly analgesics and anti-inflammatories, which help relieve discomfort and reduce inflammation, and should be used with the medical indication.
Home measures such as resting and ice packs should also be taken as they are natural ways to reduce inflammation and pain, swelling, redness, and difficulty moving the affected area, being common in the shoulder, hip, elbow and knee, for example.
Inflammation that occurs in bursitis can have several causes, such as strokes, repetitive stress, arthritis or infections, and may occur due to worsening tendinitis, and the most indicated remedies are prescribed by the orthopedist, after evaluation and confirmation of diagnosis:
1. Anti-inflammatory tablets
Anti-inflammatories, such as Diclofenac, Nimesulide, Ketoprofen, tablets or injectables, for example, are prescribed by the general practitioner or orthopaedist as they block the reaction of the body that causes the inflammation and symptoms.
Avoid using the anti-inflammatories for more than 7 to 10 days, or repeatedly, as they may cause side reactions in the body, such as kidney damage or ulcers in the stomach, for example. Therefore, if the pain persists, it is recommended to ask the doctor for further advice on how to continue the treatment.
2. Anti-inflammatory ointments
Anti-inflammatory ointments, in gel or cream forms such as Cataflan or Diclofenac, for example, may have a good local effect, and may be passed in the affected site 3 to 4 times a day.
Thus, like the tablets, anti-inflammatory ointments should not be used continuously, and should usually be for up to 14 days or according to medical advice.
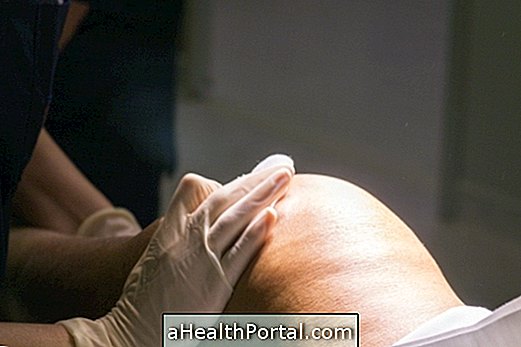
3. Corticosteroid injections
Corticosteroid injections, such as methylprednisolone or triamcinolone, for example in combination with 1-2% lidocaine, are often used by the physician in cases of bursitis that do not improve with treatment or chronic bursitis.
This medicine is injected to have a more direct effect inside the inflamed joint, which may be more effective than other forms of treatment.
4. Muscle relaxants
Muscle relaxants, such as Cyclobenzaprine, are also useful for treating bursitis, as there may be muscle strain during the frame, which further worsens the pain and discomfort for mobilizing the site.
5. Antibiotics
Antibiotic medicines, such as Ceftriaxone, Gentamicin and Penicillin, are used in case of suspected infection as a cause of bursitis, and should be doctor-directed.
Generally, with the suspicion of infection, the doctor may also request the collection of fluid from the joint, to do a laboratory examination and identify the microorganism.

Home Treatment Options
An excellent home remedy for acute bursitis is to apply ice packs to the affected joint for 15 to 20 minutes, about 4 times a day for 3 to 5 days.
This treatment will have a better effect in the acute phase of inflammation, especially when there is pain, swelling and redness. At this stage, it is also important to rest, so that the movement of the joint does not make the frame worse.
Some physical therapy exercises can also be done at home, stretching, flexibility and proprioception, which help in recovery. Check out some shoulder proprioception exercises to do at home.
In addition, the treatment can also be complemented with the use of natural remedies referred by the nutritionist in the following video:

When to do physiotherapy
Ideally, physical therapy should be done in all cases of bursitis or tendinitis, since the acute phase, in addition to being very important in chronic bursitis.
Physical therapy is done with techniques and exercises to increase mobility of the affected joint and muscle stretching to improve its function, ideally at least 2 times a week or daily.












.png)


