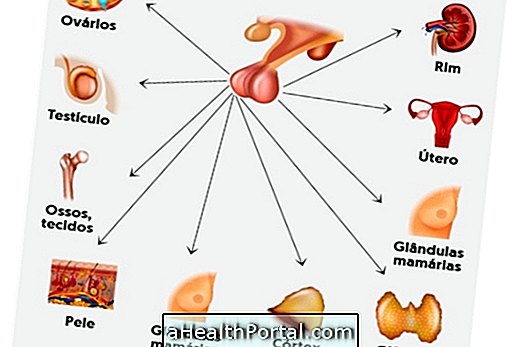
The tumor in the pituitary or pituitary tumor consists of the growth of an abnormal mass that appears in the pituitary, located at the base of the brain. The pituitary gland is a master gland responsible for controlling other glands in the body to produce hormones, so when a tumor appears in this region, various symptoms may be present, such as changes in the thyroid, infertility or increased pressure, for example.
Generally, tumors in the pituitary gland are benign and therefore can not be considered cancer, they are called pituitary adenomas, but these can also cause serious health problems because many of them produce excess hormones, affecting the whole body, and therefore be evaluated by the neurologist and treated appropriately.
Does pituitary tumor have a cure?
Benign tumors of the pituitary gland do not spread through the body because they are not carcinoma, and usually remain located in the Turkish saddle, which is a small space where the pituitary gland meets, however, they may grow and press neighboring areas like vessels blood, nerves and sinuses, but are usually easy to treat and can be completely eliminated, with great chances of healing.
Symptoms of pituitary tumor
Symptoms of pituitary tumor depend on its size and location, but may be:
Tumor in anterior pituitary (more frequent)
- Exaggerated growth of organs or bones, called acromegaly, due to increased growth hormone (GH) production;
- Hyperthyroidism due to the increase of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), which regulates the thyroid;
- Rapid weight gain and fat accumulation due to increased production of ACTH hormone leading to Cushing's disease;
- Decreased production of ova or spermatozoa, which may cause infertility due to changes in the production of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH);
- Production of whitish liquid by the nipple, in cases of prolactin-producing tumor, leading to high prolactin, which leads to the production of breast milk, even without being pregnant. Its effect on men is unknown.
Tumor in the posterior pituitary (rare)
- Frequent urge to urinate and increased pressure due to the presence of Diabetes insipidus, caused by the increase of antidiuretic hormone (ADH);
- Uterine cramps, due to increased oxytocin, leading to uterine contraction.
In addition, other symptoms such as intense and frequent headache, vision problems, excessive tiredness, nausea and vomiting may also occur, especially if the tumor is causing pressure on other parts of the brain.
Symptoms of macroadenoma
When the pituitary tumor is more than 1cm in diameter it is considered a macroadenoma, and in this case it may press other areas of the brain, such as the optic nerve or chiasm, causing symptoms such as:
- Strabismus, which is when the eyes are not properly adjusted;
- Blurred or double vision;
- Decreased vision, with loss of peripheral vision;
- Headache;
- Pain or numbness in the face;
- Dizziness or fainting.
Learn about the other signs of brain tumor in: Symptoms of brain tumor.

Diagnosis of pituitary tumor
The diagnosis of pituitary tumor is made based on the symptoms that the person presents and through blood tests, and imaging tests such as MRI or CT scan, in some cases the doctor may request a biopsy, but there is not always a need to carry out the latter.
Small pituitary adenomas that do not produce excess hormones and that are discovered accidentally, when performing an MRI or computed tomography may not require specific treatment, being necessary only to perform examinations every 6 months or 1 year, to verify if it has not increased in size, pressing other areas of the brain.
What causes tumor in the pituitary gland
The causes of tumor in the pituitary are due to the genetic predisposition that the person possesses, due to changes in his own DNA, and this type of tumor is not frequent in the same family, not being hereditary.
There are no known environmental causes or other factors related to the development of this type of tumor, whether benign or malignant, and there is nothing the person could have done to have or not have this tumor.
What is the treatment for tumor in the pituitary gland?
The treatment can completely cure the pituitary tumor, it must be guided by a neurosurgeon and is usually started with surgery to remove the tumor through the nose or a cut in the skull, which has a 80% chance of success. When the tumor is very large and is affecting other regions of the brain there are more risks of injuring brain tissue, being a more risky procedure. Complications during or after surgery, such as bleeding, infections or reactions to anesthesia are rare, but they can happen.
However, if the tumor on the pituitary gland is not very large, radiation therapy or hormonal remedies, such as Parlodel or Sandostatin, may be used to prevent or regrow growth. When the tumor is large, the doctor may choose to start treatment with radiotherapy or drugs to reduce the size of the tumor, and then make a withdrawal through surgery.
The follow-up of the case can be done by the neurologist or endocrinologist with examinations that must be performed regularly to check the general health of the person.













-e-como-tratar.jpg)