The symptoms of mouth cancer vary according to the degree of development of the disease, such as the appearance of wounds or canker sores, pain around the tooth and persistent bad breath. Signs and symptoms may occur anywhere in the mouth but are most often seen in the posterior region of the tongue, cheeks, gums and the roof of the mouth.
Mouth cancer is a type of tumor, usually diagnosed by the dentist, and that when not treated properly, can be fatal. Learn more about mouth cancer.
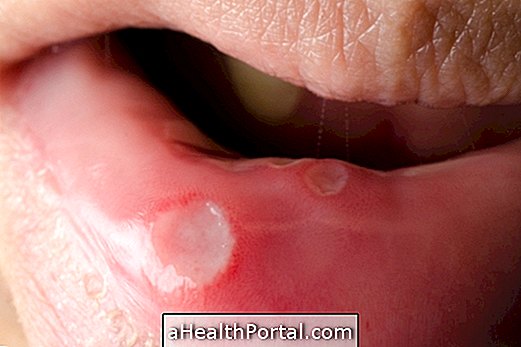
Signs and Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
The symptoms of mouth cancer appear silently, and because there is no pain, the person may be slow to seek treatment, the disease being diagnosed, most often, in more advanced stages. Signs and symptoms indicative of oral cancer vary according to the degree of disease development, with the first signs being:
- Wound or canker sores in the oral cavity that do not heal in 15 days;
- Red or white spots on the gums, tongue, lips, throat or mouth lining;
- Small superficial wounds that do not hurt and may or may not bleed;
- Irritation, sore throat or feeling that something is stuck in the throat.
However, in later stages, symptoms progress to:
- Difficulty or pain when speaking, chewing and swallowing;
- Lumps in the neck due to the increase of the gums;
- Pain around the teeth, which can fall easily;
- Persistent bad breath;
- Sudden weight loss.
If these signs and symptoms of oral cancer persist for more than 2 weeks, it is recommended to consult a general practitioner or a dentist to evaluate the problem, take the necessary tests and diagnose the disease, and initiate appropriate treatment.
Mouth cancer can arise due to a person's habits, such as smoking and drinking excessively; in addition, HPV virus infection can result in oral manifestations, increasing the chance of the occurrence of cancer of the mouth. Poor vitamin and mineral nutrition and prolonged exposure to the sun may also favor the occurrence of oral cancer. Understand how each of these factors can cause oral cancer.
How is the diagnosis made?
In most cases, the doctor is able to identify the cancer lesions just by observing the mouth, however, it is common to ask for a biopsy of a small piece of the lesion to identify if there are cancerous cells.
If tumor cells are identified, the doctor may also order a CT scan to assess the degree of disease development and to identify whether there are other affected sites other than the mouth. Know the tests that identify the cancer.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for mouth cancer can be done through surgery to remove the tumor, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. The choice of the best treatment is done according to the location of the tumor, severity and whether or not the cancer has spread to other parts of the body. Learn more about how this type of cancer is treated.