Anesthesia is a strategy used to prevent pain or any sensation during a surgery or painful procedure through the administration of medications through the vein or through inhalation. Anesthesia is usually performed in more invasive procedures or that may cause any type of discomfort or pain in the patient, such as heart surgery, childbirth or dental procedures, for example.
There are several types of anesthesia, which affect the nervous system in various ways by blocking nerve impulses, the choice of which will depend on the type of medical procedure and the state of health of the person. It is important that any type of chronic illness or allergy is advised to the doctor so that the best type of anesthesia is indicated without any risk. See what the care is before surgery.
1. General anesthesia
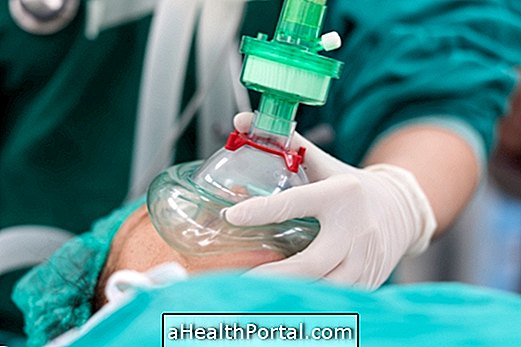
During general anesthesia, anesthetic drugs are administered that sedate the person deeply, so that the surgery performed, such as heart, lung or abdominal surgery, does not cause any pain or discomfort.
The medications used leave the person unconscious and insensitive to pain, promoting muscle relaxation and causing amnesia, so that everything that happens during surgery is forgotten by the patient.
The anesthetic can be injected into the vein, having an immediate effect, or inhaled through a mask in the form of gas, reaching the bloodstream through the lungs. The duration of its effect is variable, being determined by the anesthesiologist, who decides the amount of anesthetic medicine to be administered. Learn more about general anesthesia.
The drugs most commonly used in general anesthesia are: benzodiazepines, narcotics, sedatives and hypnotics, muscle relaxants and halogenated gases.
What are the risks
Although anesthesia is a fairly safe procedure, it may have some associated risks depending on some factors, such as the type of surgery and the person's medical condition. The most common side effects are nausea, vomiting, headache and allergies to the anesthetic drug.
In more severe cases, complications such as stopping breathing, cardiac arrest or even neurological sequelae in people with poorer health due to malnutrition, heart, lung or kidney problems, for example.
Although it is very rare, it can happen that the anesthesia has a partial effect, like taking the conscience but allowing the person to move or the person can not move but feel the events around him.
2. Local anesthesia

Local anesthesia involves a very specific area of the body, does not affect consciousness and is usually used in small surgeries such as dental procedures, eye, nose or throat surgery, or in conjunction with other anesthesia, such as regional or sedation anesthesia.
This type of anesthesia can be administered in two ways, by applying an anesthetic cream or spray to a small region of the skin or mucosa, or by injecting the anesthetic drug into the tissue to be anesthetized. Lidocaine is the most common local anesthetic.
What are the risks
Local anesthesia, when used correctly, is safe and has almost no side effects. However, at high doses it can have toxic effects, which can affect the heart and breathing or compromise brain function, since high doses can reach the bloodstream.
3. Regional anesthesia

Regional anesthesia is used when it is necessary to anesthetize only a part of the body, such as an arm or a leg, for example, and there are several types of regional anesthesia:
Spinal anesthesia
In spinal anesthesia, the local anesthetic is administered with a fine needle in the fluid that bathes the spinal cord, called cerebrospinal fluid. In this type of anesthetic the anesthetic mixes with the spinal fluid and contacts the nerves, leading to loss of sensitivity of the lower limbs and the lower abdomen.
Epidural anesthesia
Also known as epidural anesthesia, this procedure blocks the pain and sensations of only one region of the body, usually from the waist down.
In this type of anesthesia, the local anesthetic is administered through a catheter that is placed in the epidural space that is around the spinal canal, leading to loss of sensitivity of the lower limbs and abdomen. See more about epidural anesthesia and what it does.
Peripheral nerve block
In this type of regional anesthesia, the local anesthetic is administered around the nerves responsible for the sensitivity and movement of the limb where the surgery is to be performed, and a variety of nerve blockers may be administered.
Groups of nerves, called a plexus or ganglion, that cause pain to a specific organ or body region, are then blocked leading to anesthesia of areas of the body such as the face, nose, palate, neck, shoulder, and arm.
Intravenous Regional Anesthesia
Intravenous anesthesia is a procedure in which a catheter is placed in a vein of a limb so that the local anesthetic is administered, while placing a tourniquet above the area for the anesthesia to remain in place. Sensitivity is restored when the tourniquet is removed.
Regional anesthesia is usually used during simple surgical procedures such as during a normal delivery, in small surgeries such as gynecological or aesthetic surgeries or in orthopedics, for example.
Learn how anesthesia eliminates labor pains.
What are the risks
Although rare, side effects such as excessive sweating, infection at the site of injection, systemic toxicity, heart and lung problems, chills, fever, nerve damage, perforation of the spinal cord protecting membrane, called dura mater, may occur. cause paraplegia.
4. Sedation anesthesia

Sedation anesthesia is given intravenously and is usually used in combination with local or regional anesthesia to increase the person's comfort.
Sedation may be mild, in which the person is relaxed but awake and may respond to questions from the doctor, moderate in that the person usually sleeps during the procedure, but can be easily awakened when asking a question or deep in which the person sleeps during the whole procedure, not remembering what has happened since the anesthesia was administered. Being mild, moderate or profound, this type of anesthesia is accompanied by oxygen supplementation.
What are the risks
Although rare, allergic reactions, breathing difficulties, changes in heart rhythm, nausea, vomiting, delirium, sweating and infection at the injection site may occur.