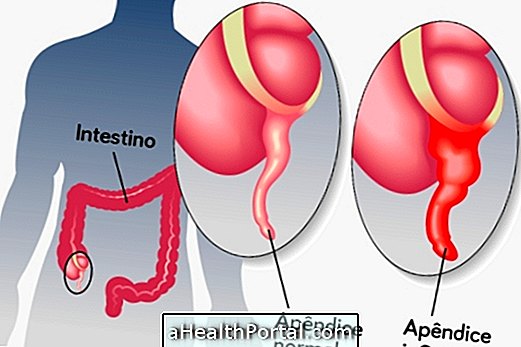
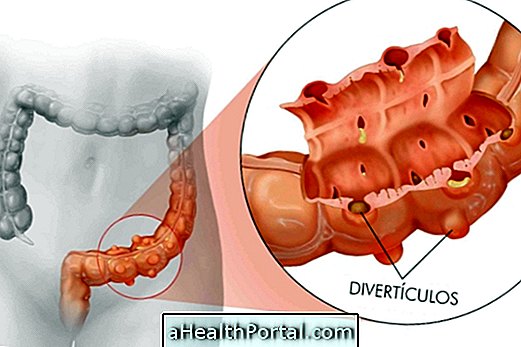
Diverticulosis, or diverticular disease, is a bowel disease characterized by the formation of diverticula, which are small pockets, in the lining of the intestine. Diverticula are formed when points in the wall of the intestine are fragile, and end up being projected to the outside due to intestinal contractions.
These small pouches may range from 2.5 mm to 2.5 cm, usually appear in the late part of the large intestine and generally do not cause symptoms, however, when inflammation or infection causes the so-called diverticulitis. Learn how to identify and treat diverticulitis.
Diverticulosis can manifest itself in both men and women, more often than 60 years, and is rare in people under 40 years of age, and usually arises from a diet low in fiber.
How to identify
Diverticulosis without complications does not cause symptoms, however, if diverticula ruptures, there may be bleeding in the stool. When there is inflammation or bacterial infection, there may be colicky abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting or fever, which characterizes diverticulitis.
Anyone can develop diverticulosis, being a more common disease in the elderly, and its causes are mainly related to the malfunction of the intestine and, therefore, it is common for the person with diverticulosis to present:
- Constipation;
- Abdominal swelling;
- Diet low in fiber and rich in red meat and fat;
- Sedentary lifestyle.
In addition, people who smoke may present a greater risk for the formation of diverticula, since smoking may favor the fragility of the intestinal walls.
How is the diagnosis made?
Diverticulosis can arise and remain for many years without causing symptoms and without being discovered, so it is often observed accidentally in a routine colonoscopy, for example.
However, when there is complication of the disease, with bleeding or progression to diverticulitis, examinations such as ultrasound or tomography of the abdomen may be necessary to assess the level of abdominal involvement and to schedule the best type of treatment.
How to treat
The treatment for diverticulosis is mainly made with a diet rich in fibers, present in fruits, vegetables and vegetables. Food supplements high in fiber, such as Metamucil, may also be useful to improve bowel functioning.
In addition, in the case of cramps, the use of anti-spasmodics and analgesics such as Butylscopolamine and Paracetamol may be helpful in relieving the symptoms. Check out the main treatment options for diverticulosis.
However, if there is diverticulitis, antibiotics and a dietary restriction may be needed for bowel rest. In more severe cases, with recurrent or complications, surgery may be indicated, consisting of removal of the part of the intestine where the diverticula are located. Also check out the main ways to treat diverticulitis.