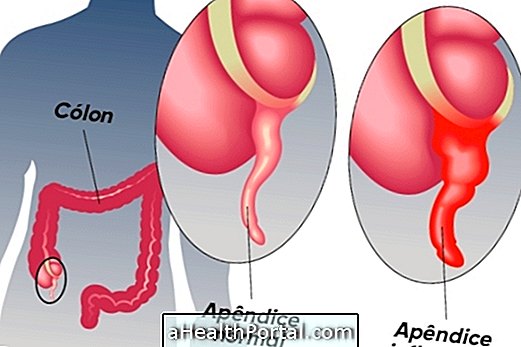
Acute appendicitis corresponds to inflammation of the cecal appendix, which is a small structure located on the right side of the abdomen and attached to the large intestine. This condition usually happens due to obstruction of the organ mainly by stool, resulting in symptoms such as abdominal pain, low fever and nausea, for example.
Due to the obstruction, there may still be a proliferation of bacteria, also characterizing an infectious condition that if not treated properly can progress to a sepsis. Understand sepsis.
In the case of suspected appendicitis, it is important to go to the hospital as soon as possible, as there may be perforation of the appendix, characterizing suppurative appendicitis, which may put the patient at risk. Learn more about appendicitis.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms that indicate acute appendicitis are:
- Abdominal pain on the right side and around the navel;
- Abdominal distension;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Low fever, up to 38ºC, unless there is perforation of the appendix, having a high fever;
- Loss of appetite.
The diagnosis is made through physical, laboratory and imaging exams. Through the blood count, the increase in the number of leukocytes can be seen, which can also be seen in the urine test. Computed tomography and ultrasound of the abdomen also makes the diagnosis of acute appendicitis, because through these examinations it is possible to verify the structure of the appendix and identify any inflammatory signs.
Possible causes
Acute appendicitis is mainly caused by obstruction of the appendix by very dry stools. But it can also happen due to the presence of intestinal parasites, gallstones, enlargement of the lymph nodes of the region and traumatic injuries in the abdomen, for example.
In addition, acute appendicitis can occur due to genetic factors related to the position of the appendix.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for acute appendicitis is usually done by surgically removing the appendix in order to avoid complications and possible infections. The hospitalization time is 1 to 2 days, and the patient is released for physical exercise and other day-to-day activities after 3 months of surgery. Learn how surgery for appendicitis is done.
Often the doctor also indicates the use of anti-inflammatories and antibiotics before and after surgery.
Complications of acute appendicitis
If acute appendicitis is not identified quickly or treatment is not done correctly, there may be some complications, such as:
- Abscess, which is the excess of pus accumulated around the appendix;
- Peritonitis, which is inflammation of the cavity of the abdomen;
- Bleeding;
- Bowel obstruction;
- Fistula in which an abnormal connection occurs between an abdominal organ and the surface of the skin;
- Sepsis, which is a serious infection of the whole organism.
These complications usually occur when the appendix is not removed in time and breaks.