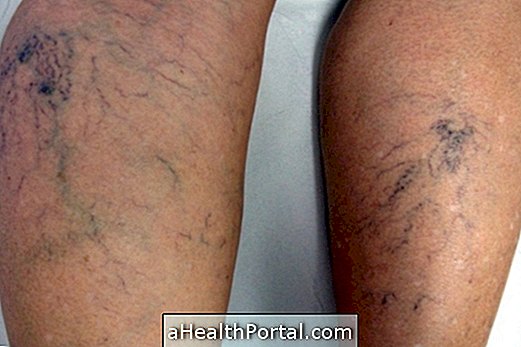
Varicose veins are dilated veins that can be easily seen beneath the skin, which arise especially in the legs, causing pain and discomfort. They can be caused by poor circulation, especially during pregnancy and menopause, but it especially affects the elderly.
Varicose veins occur more often in women, but may also appear in men, because the factors that influence the occurrence of varicose veins are very diverse, and may be caused by the person sitting or standing for a long time, for example. The diagnosis of varicose veins is usually done by the angiologist or vascular surgeon according to the characteristics of the varicose veins and associated symptoms.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of varicose veins can be done by improving the blood circulation, changing habits of life, taking medicine for varicose veins or by doing treatments such as applying substances directly to the varice or surgery in the most serious cases. In the case of varicose veins that cause a lot of pain in the legs the treatment can be done through:
- Sclerotherapy, which is a treatment that consists of applying substances directly into the varix or laser to remove the varicose veins and relieve the symptoms;
- Surgery, which is indicated when varicose veins have large caliber and cause symptoms like pain, itching and swelling in the legs that can compromise the movement.
The choice of treatment is made by the angiologist or vascular surgeon, in which the location of varice occurrence, size and associated symptoms is analyzed. Learn more about varicose vein treatment.
In addition, some doctor's recommendations to be adopted after treatment or to prevent varicose veins are:
- Wear elastic compression stockings under medical guidance as they improve venous return and decrease the chances of varicose veins occurring or coming back;
- Use varicose vein medications such as Varicocell and Antistax according to medical advice - See other remedies for varicose veins treatment.
- Put a wedge in the foot on the bed to facilitate the return of blood to the heart;
- Exercise regularly with the guidance of a professional;
- Do lymphatic drainage 3 times a week;
- Eat foods like horse chestnut, which improves blood circulation;
- Sit up and lie down with your legs up;
Also, it is important to avoid wearing high heels, sitting or standing for a long time, as these situations may favor the appearance of varicose veins.
Home treatment
The home treatment for varicose veins consists of the use of natural medicines, such as Novarrutina, for example, as it has substances capable of relieving pain and swelling of the legs. In addition, compresses can be made with cabbage and thistle-marian tea, as they can reduce symptoms and bring a sense of well-being. See 8 home remedies for varicose veins.
Possible Complications
When varicose veins are not treated correctly, there may be complications such as dermatitis, eczema, leg ulcers, thrombophlebitis, pain and deep venous thrombosis, which is a severe condition in which thrombi (clots) form in the leg veins that may hinder or block the passage of blood. Learn more about deep venous thrombosis.

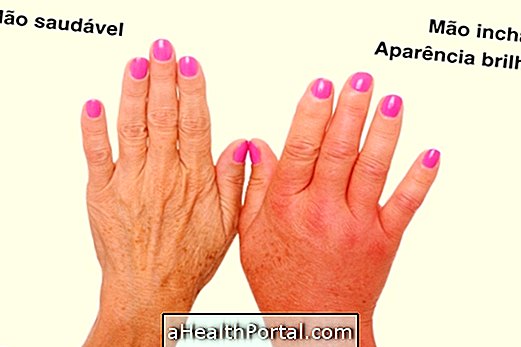
Main symptoms of varicose veins
The main symptoms that occur in varicose veins are:
- Feeling of weight in the legs;
- Tingling;
- Sensitivity in the region;
- Dark spots on the leg;
- Itching.
It is important to note the characteristics of the varicose veins as well as the associated symptoms so that the orientation of the treatment by the doctor is as correct as possible.
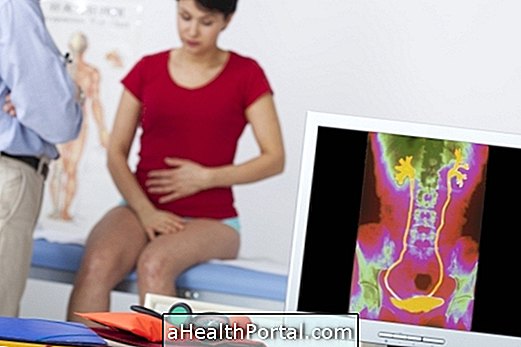
Pelvic varices
Pelvic varices have the same cause of varicose veins in the legs, however, they are located in the pelvic region, that is, they arise around the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries, causing intense abdominal pain in the woman. This pain can be felt during after intercourse, feeling of weight in the intima, increased menstrual flow and urinary incontinence. Here's how to identify and treat pelvic varicose veins.
Pelvic varices can be identified by tomography of the abdomen or pelvic region, angioresonance or phlebography, which is a kind of x-ray that allows the visualization of the veins after the injection of a contrast.
Esophageal varices
Esophageal varices usually have no symptoms, but when they bleed it can lead to vomiting of blood, blood in the stool, dizziness and loss of consciousness. This type of varicose vein usually occurs due to liver cirrhosis, which obstructs the circulation of the portal system and increases the venous pressure in the esophagus.
The diagnosis of esophageal varices can be made by digestive endoscopy and imaging tests such as computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging. Learn how to treat varicose veins in the esophagus.
Main causes
Varicose veins are more common to occur in pregnant or menopausal women, but may occur less often in men. Some situations that can influence the occurrence of varicose veins are:
- Use of contraceptives;
- Obesity;
- Sedentary lifestyle;
- Professional activity, because sitting or standing for a long time can lead to the appearance of varicose veins.
In addition, varicose veins may be the result of genetic factors, being considered a hereditary condition.
Varicose veins in pregnancy
The onset of varicose veins in pregnancy is normal and is due to weight gain, belly growth due to hormonal changes and due to increased difficulty in blood circulation. Varicose veins in pregnancy can arise in the legs and feet, groin, uterus and anal area, which are hemorrhoids.
What can be done to relieve the discomfort of varicose veins in pregnancy is to wear therapeutic pantyhose, avoid standing too long or sitting with your feet on the floor, drink plenty of water and put a shim at the foot of the bed. The use of varicose vein remedies during pregnancy is contraindicated.