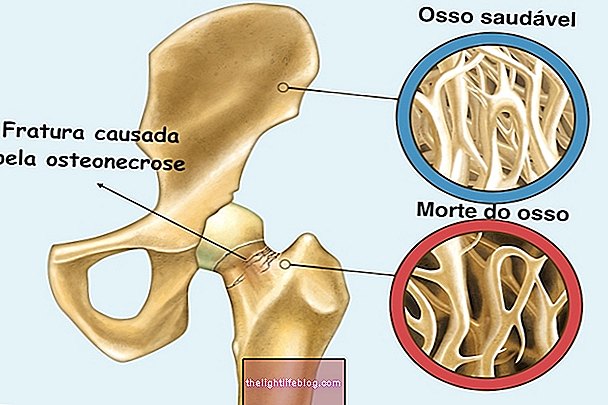
Spondylosis is a situation where there is a small fracture of a spinal vertebra, which usually worsens giving rise to a spondylolisthesis, which is when the intervertebral disc 'slides' backward, deforming the spine, being able to press a nerve and cause symptoms such as back pain and difficulty moving.
This situation is not exactly the same as a herniated disc, because in the hernia only the disc is affected, being compressed. In the case of spondylosis one (or more) vertebrae of the spine 'slide backwards' due to a fracture of the vertebral pedicle and shortly afterwards also the intervertebral disc accompanies this movement, coming back, causing back pain and tingling sensation. However, in some cases it is possible to have spondylolisthesis with a herniated disc at the same time.
Spondylosis and spondylolisthesis are more common in the cervical and lumbar regions, but can also affect the thoracic spine. Definitive healing can be achieved with surgery that repositions the spine in its original location, but remedy and physical therapy treatments may be sufficient for pain relief.
Symptoms of spondylosis and spondylolisthesis
Spondylosis, which is the initial phase of the spinal cord injury, may not produce symptoms, being discovered accidentally when performing an x-ray or tomography scan of the back, for example. When the spondylolisthesis is formed, and the situation is more severe, the symptoms may be:
- Intense back pain at the affected site: back or neck area;
- Difficulty in performing movements, including walking and practicing physical activity;
- Lumbar pain can radiate to the buttock or legs and is characterized as sciatic pain;
- Feeling of tingling in the arms, in cases of cervical spondylolisthesis and in the legs, in case of lumbar spondylilostosis.
The diagnosis of spondylolisthesis is made through an MRI that shows the exact position of the intervertebral disc. Usually the diagnosis is made after 48 years, being the women most affected.
What causes
The most common causes of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis are:
- Malformation of the spine : These are usually changes in spinal position that arise from birth and facilitate the displacement of a vertebra during adolescence when practicing artistic or rhythmic gymnastics, for example.
- Strokes and traumas in the spine : they can cause deviation of a spine vertebra, especially in traffic accidents;
- Diseases of the spine or bones : diseases like osteoporosis can increase the risk of a displacement of a vertebra, being a common condition of aging.
Both spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis are more common in the lumbar and cervical regions, causing pain in the back or neck, respectively. Spondylolisthesis can be disabling when it is severe and the treatments do not bring the expected pain relief, in which case the person may have to retire.
How is the treatment done?

Treatment for spondylosis or spondylolisthesis varies according to the intensity of the symptoms and the degree of displacement of the vertebra, which can vary from 1 to 4, and can be done with anti-inflammatory, muscle relaxant or analgesic remedies, but also acupuncture and physical therapy, and when none of these options is sufficient to control pain, surgery is indicated. The use of a vest was formerly used, but has not been recommended by doctors.
In case of spondylosis it may be recommended to take Paracetamol, which is effective in controlling pain. In the case of spondylolisthesis, when the deviation is only grade 1 or 2, and therefore the treatment is only done with:
- Use of anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Ibuprofen or Naproxen: decrease inflammation of the discs of the vertebrae, relieving pain and discomfort.
- Injections of corticosteroids, such as Dexacitoneurin or Hydrocortisone: are applied directly to the site of the displaced vertebrae to quickly relieve inflammation. Need to be done between 3 to 5 doses, repeated every 5 days.
Surgery to strengthen the vertebra or to decompress the nerve is only done in cases of grade 3 or 4, where it is not possible to control the symptoms with medication and physical therapy, for example.
When and how physiotherapy is done
Physiotherapy sessions for spondylosis and spondylolisthesis help complete drug treatment, allowing pain relief faster and reducing the need for higher doses.
In physical therapy sessions exercises are performed that increase the stability of the spine and increase the strength of the abdominal muscles, decreasing the movement of the vertebrae, facilitating the reduction of inflammation and, consequently, relieving pain.
Electronic equipment may be used for pain relief, manual therapy techniques, lumbar stabilization exercises, abdominal strengthening, ischiatibial stretching, located at the back of the legs. And RPG, Pilates Clinic and Hydrokinesiotherapy exercises, for example, can also be recommended.