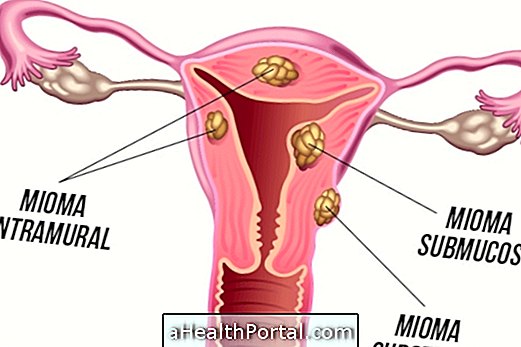
Uterine fibroids are benign tumors formed in the muscle tissue that forms the uterus and are therefore also called fibroids or uterine leiomyomas. Its location in the womb may vary as well as its size, which can be from microscopic to large like a melon.
These tumors are very common and usually do not cause symptoms but when they appear they can be cramps, bleeding or difficulty getting pregnant.
The main types of myoma of the uterus are divided by its location in this organ, and can be:
- Subserous, when it appears in the outer part of the uterus;
- Intramural, when it appears inside the walls of the uterus;
- Submucous, when it is inside, inside the cavity of the uterus.
Understand the types of uterine fibroid.
The best strategy for curing myoma is removal of the uterus, but when this is not an option, other treatments indicated by the gynecologist may be indicated. In these cases, myoma may or may not recur.
Main symptoms
Some women may have symptoms, which vary according to the amount, type, and size of myoma. The main ones are:
- Increased blood loss in menstruation;
- Prolonged menstrual period;
- Abdominal pain or cramps;
- Increase in the volume of the uterus and abdominal region;
- Symptoms of constipation;
- Willingness to urinate more often or urinary incontinence;
- Pains during intimate contact;
- Difficulty getting pregnant.
This disease is diagnosed by the gynecologist and through examinations such as ultrasound or other imaging tests, such as hysteroscopy and hysterosalpingography, which evaluate the cavity of the uterus.
In addition, women with uterine fibroid who wish to become pregnant, even if they have no symptoms, should be followed up with the gynecologist, because the presence of this tumor may bring some complications during pregnancy, such as abortions.
Learn how fibroid treatment can be done during pregnancy.
Causes of myoma
The cause of the onset of uterine fibroids has not yet been fully elucidated. When it appears, it is because some cells of the muscle tissue that form the uterus multiply inordinately, giving rise to the tumor.
It is known that the hormones of women have influence on their development, because the symptoms appear in adult women and usually regress after the menopause. In addition, it can happen that the symptoms of this disease reappear in women undergoing hormone replacement therapy.
Women who are more likely to have myoma are those who do not have children, who have a diet rich in red meat and vegetables, obese women and those with a history of this disease in the family.

When you need to treat
Treatment is indicated when the woman has severe symptoms, such as a lot of pain or heavy menstruation, or when trying to get pregnant without success. The type of treatment depends on the symptoms, the size and the type of myoma of each woman, and must be guided by the gynecologist. In many cases, since they do not cause symptoms, routine follow-up is only done.
Treatment to cure myoma can be done through surgery or other techniques done by the gynecologist, such as embolization or cauterization of the uterine wall. The use of hormonal medications, such as the contraceptive pill, to prevent its growth, and may also be indicated by the gynecologist.
Anti-inflammatory drugs may also be used to relieve symptoms, such as ibuprofen.
Learn more details of myoma treatment.
Mioma makes it hard for a woman to get pregnant
A small number of women who have myoma may have difficulty becoming pregnant because myoma may cause some deformities of the inside of the uterus, as well as changes in circulation and increased inflammation.
In these cases, it is possible to perform treatments with hormone-based remedies, such as estrogens and androgens, or surgeries, which are myomectomy or fibroid embolization to increase the chances of becoming pregnant.