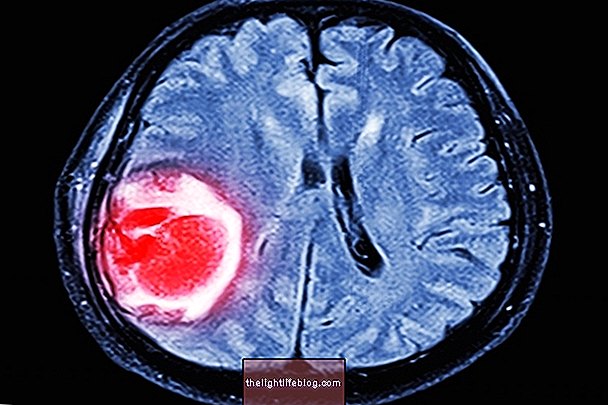
AIDS-related illnesses are those that affect HIV-positive patients because of the weakness of their immune system, such as Tuberculosis, Pneumonia, or Lymphoma, for example.
Not all are serious and can be controlled, but whenever the patient presents any of them the treatment must be redoubled because in addition to the antiretrovirals, it is essential to combat the opportunistic infection to guarantee the life of the patient.
Some examples of AIDS-related diseases are:
Respiratory diseases | Gripes and colds are common and simpler to resolve, but the patient may also have more serious illnesses such as tuberculosis or pneumonia. |
|
Skin diseases | Kaposi's sarcoma; Mycoses; Purple; Stomatitis. |
Infectious diseases | Cytomegalovirus; Neurotoxoplasmosis; Persistent candidiasis; Encephalopathy; Chagas disease; Extrapulmonary cryptococcosis. |
Cardiovascular diseases | Predisposition to accumulate fat inside the arteries and may cause atherosclerosis, stroke or infarction. |
Renal diseases | Renal calculus and renal failure. |
Cancer | The most common is lymphoma. |
Weight Loss Syndrome
It is a term that refers to loss of 10% or more of weight without apparent cause. It can happen because of the metabolic changes caused by the virus, other opportunistic infections or as a side effect of the medicines.
Many AIDS patients also have neurological problems such as memory problems, memory loss, poor concentration, and difficulty performing complex tasks.
Treatment of AIDS-related diseases
Treatment of AIDS-related illnesses should be done with the use of medications prescribed by the physician for infection control, in addition to antiretroviral therapy, with the use of the cocktail. However, it is possible that there is drug interaction and to decrease the patient's unpleasant symptoms the doctor may indicate the use of other medications.
Treatment can sometimes be done at home, but many doctors recommend hospitalization for better control of the infection, increasing the chances of cure. After controlling for the disease, the doctor may recommend that the patient receive antiretroviral therapy only and perform the AIDS tests to confirm the concentration of lymphocytes and CD4 in the blood.
To help identify the disease, see what are the main symptoms of AIDS.