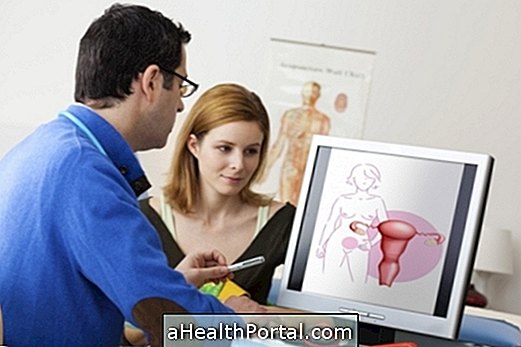
Hysteroscopy is a gynecological exam that allows you to identify possible changes within the uterus.
In this examination a tube called the hysteroscope, approximately 10 millimeters in diameter, is inserted through the vagina into the cervix, as shown in the image. This tube contains an optical fiber that transmits light, allowing visualization of the cavity of the uterus.
There are 2 types of hysteroscopy:
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy aims to visualize the uterus internally to diagnose possible changes or diseases. Learn more about diagnostic hysteroscopy;
- Surgical hysteroscopy aims to treat changes within the uterus. Thus, surgical hysteroscopy is indicated for the treatment of polyps, fibroids, thickening of the endometrium, malformations of the uterine cavity, among other problems. Understand how surgical hysteroscopy is done.
Hysteroscopy should be performed during the first fortnight of menstruation when the woman is no longer menstruating and can not be done during pregnancy and in the presence of a vaginal infection.
This examination is carried out in gynecological and obstetrical hospitals or clinics, by the gynecologist, and can be done by SUS, some health plans or privately, costing an average of 100 and 400 reais, depending on the place where it is done and is for diagnosis or surgery.


Does hysteroscopy hurt?
Hysteroscopy may hurt and cause discomfort in a woman, but usually the test is well tolerated.
What is it for
- Hysteroscopy may be indicated for diagnosis or treatment of the following conditions:
- Identify or remove endometrial uterine polyp;
- Identify and remove submucosal uterine fibroids;
- Endometrial thickening;
- Evaluation of uterine bleeding;
- Evaluation of causes of infertility;
- Investigate defects in the anatomy of the uterus;
- Performing tubal ligation surgery;
- Investigate the existence of cancer in the uterus.
In addition, hysteroscopy is also indicated to indicate or control surgeries performed in the uterus.
Hysterosalpingography is an exam that is also widely used to identify changes in the uterus and fallopian tubes. However, it uses a different technique, with the injection of contrast in the uterus and x-rays, which can demonstrate the anatomy of these organs. Learn more about how it is done and what hysterosalpingography is for.