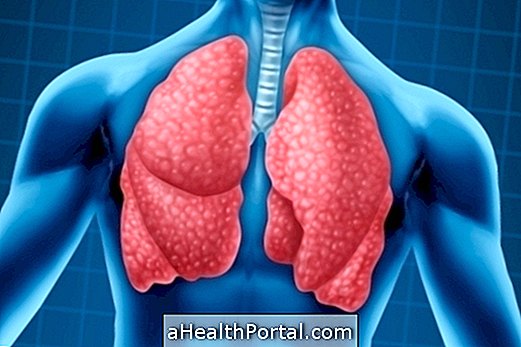
Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the pulmonary bronchi, the place where air passes into the lung, which persists for more than 3 months, even with seemingly adequate treatment. It is more common in smokers and increases the risk of diseases like pulmonary emphysema, for example.
Treatment for chronic bronchitis
Treatment for chronic bronchitis can be done through the use of bronchodilator medications such as Salbutamol, under the guidance of the pulmonologist.
Physical therapy is very useful for the treatment of chronic bronchitis as it can improve gas exchange, improve respiratory capacity and eliminate secretions. But in addition it is crucial to discover its cause and then eliminate it so that it can reach the cure of the disease.
Does chronic bronchitis have a cure?
Chronic bronchitis does not always have a cure, especially if the individual has some other chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - COPD or if they are smokers. But if the individual respects all doctor's guidelines, there are good chances of cure for chronic bronchitis.
Is Chronic Bronchitis Contagious?
Chronic bronchitis is not contagious and therefore does not risk contamination when it is close to the patient with the disease.
Symptoms of chronic bronchitis
Symptoms of chronic bronchitis:
- Difficulty breathing;
- Cough that can be dry or productive;
- Wheezing: wheezing on the chest;
- Tiredness;
- Nails and lips may appear purplish.
In the case of chronic bronchitis, these symptoms should be present for more than 3 months.
Causes of chronic bronchitis
The causes of chronic bronchitis can be:
- Cigarette;
- Pollution;
- Inhalation of toxic substances;
- Always be in contact with substances that cause allergy in the individual.
The diagnosis of chronic bronchitis is made by the pulmonologist after checking the evolution of the disease.
Useful link:
- Pulmonary emphysema