Toxicocariasis is a parasitic disease caused by the parasite Toxocara sp., which can inhabit the small intestine of cats and dogs and reach the human body through contact with feces contaminated by feces of infected dogs and cats, and may result in abdominal pain, fever or decreased vision, for example.
This disease is also known as larva migrans, which can be classified according to the place of migration of the larva through the body in:
- Visceral larva migrans or visceral toxocariasis, in which the parasite migrates to the viscera, where it can reach adult life;
- Larva migrans ocular or ocular toxocariasis, in which the parasite migrates the eyeball.
Generally, human toxocariasis is more common in children who play on the ground, on the ground or in the sand, but may also occur in adults after eating rabbit meat or undercooked lamb.
Human toxocariasis is cured by ingestion of antiparasitics, but the most important is to prevent the disease, leading domestic animals to be treated at the veterinarian against animal toxocariasis.
Main symptoms
The symptoms of toxocariasis vary according to the affected part of the body, so when the larva reaches the liver, heart, lungs, brain or muscles, the disease is called visceral toxocariasis, whose symptoms vary according to the amount of larvae present in the body and the person's immune response, the main symptoms being:
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Persistent cough;
- Wheezing and difficulty breathing;
- Abdominal pain;
- Liver enlargement, also called hepatomegaly;
- Hypereosinophilia, which corresponds to the increase in the amount of eosinophils in the blood;
- Cutaneous manifestations, such as pruritus, eczema and vasculitis.
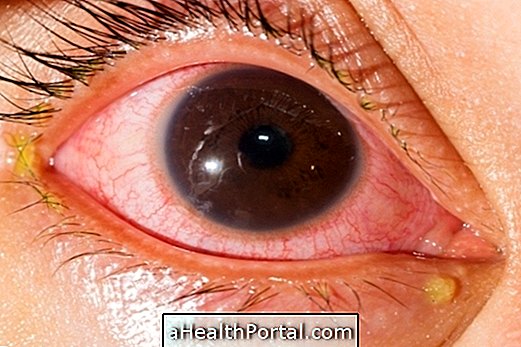
When the larvae affect the eyes, it causes ocular toxocariasis, which may cause some symptoms such as:
- Redness of the eye;
- Pain or itching in the eye;
- White spots on the pupil;
- Decreased vision.
Thus, when there is a suspicion of toxocariasis infection, it is recommended to consult the general practitioner, in the case of the adult, or the pediatrician, in the case of the child, to make the diagnosis and start the treatment.
The diagnosis of toxocariasis is difficult, since it is usually only confirmed after identification of the larvae by tissue biopsy. However, it is possible to detect the presence of antibodies against the parasite in the patient's bloodstream by means of immunological and serological tests and may be very useful in the diagnosis.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for human toxocariasis should be directed by the general practitioner or by a pediatrician, but is usually done with the intake of antiparasitic medicines, such as Albendazole, Thiabendazole or Mebendazole, 2 times a day for 5 days or according to a medical recommendation. See what the main remedies are for me and how they work.
In addition, in the case of visceral toxocariasis, the physician may also prescribe the use of corticosteroids, such as Prednisone, to reduce inflammation of the organ and relieve the patient's symptoms. In the case of ocular toxocariasis, it is also advisable to consult an ophthalmologist to start treatment avoiding the development of permanent lesions in the eye.
How to avoid toxocariasis
To avoid toxocariasis, the Ministry of Health recommends:
- Take the dogs and cats to the vet to be treated against parasitoses;
- Wash the place the animal lives at least once a week;
- Eliminate the feces of the animals daily, burying them or placing them in separate and closed bags in the bin;
- Wash hands thoroughly after contact with pets and whenever necessary;
- Prevent children from playing in places where there are domestic animals;
In addition to these recommendations, it is also important that foods, such as vegetables and meat, be well cooked, as they may be infected by Toxocara larvae. See what diseases are transmitted by animals.