The treatment of pneumonia caused by Legionella Pneumophila, also known as Legionnaire's disease, is usually done in hospital for 7 to 10 days with the injection of antibiotics prescribed by the doctor, such as:
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Azithromycin;
- Levofloxacin;
- Gemifloxacin;
- Trovofloxacin;
- Erythromycin.
Infection with this type of bacterium is very serious, so a person often needs to be admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) to keep vital signs constantly being evaluated, so as to quickly identify if the antibiotic is able to eliminate the bacteria responsible for the disease.
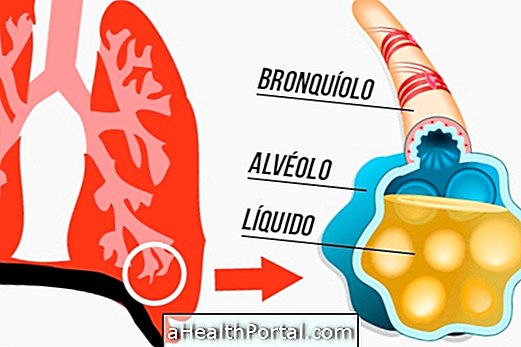
In addition, treatment usually also involves the use of continuous oxygen mask to reduce other symptoms of the disease such as difficulty breathing and shortness of breath, caused by the accumulation of secretions in the lungs. Get to know the other common legionella symptoms.
Possible Complications
The complications of Legionella arise when the treatment of pneumonia is not started as soon as possible and include worsening pneumonia, the onset of respiratory failure and even death.
Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement in pneumonia caused by Legionella Pneumophila include decreased fever and pain in the chest and head, as well as decreased shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
Signs of worsening
Signs of worsening are most common when treatment is not started quickly or the antibiotic is not being effective against the bacteria and include increased fever up to 40 ° C, increased difficulty in breathing and shortness of breath as well as worsening pain in the chest.