Prolactin is a hormone that in spite of being responsible for the production of breast milk, in man, has other functions, such as relaxing the body after reaching orgasm, for example.
Normal values of prolactin in man range from 2 to 17.7 ng / mL but may reach much higher values due to diseases, use of drugs that have this side effect, or due to a tumor in the brain.
Symptoms of prolactin increase in man
The discharge of milk from the man's nipple may be present in some cases and may be observed when the doctor presses the darker region of the breast. Other symptoms are:
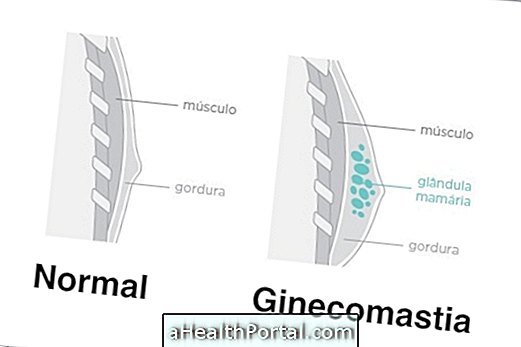
- Breast augmentation;
- Decreased sexual desire;
- Difficulty in keeping the penis erect, to maintain a satisfactory intimate contact;
- Decreased number of sperm;
- Reduction of body hairs;
- Infertility;
- Osteoporosis.
Other less common signs and symptoms are headache, changes in vision due to optic nerve atrophy, and paralysis of cranial nerves, which are more common in men than in women, probably because in men tumors are usually larger than in women .
Causes of prolactin increase in man
Some examples of remedies that lead to the increase of male prolactin are:
- Antidepressants: alprazolam, fluoxetine, paroxetine;
- Remedies for eplepsy: haloperidol, risperidone, chlorpromazine;
- Stomach and nausea medicines: cimetidine and ranitidine; metoclopramide, domperidone and cisapride;
- Remedies for high blood pressure: reserpine, verapamil, methyldopa, atenolol.
In addition to medicines, tumors of the head, brain, or pituitary gland may also cause increased prolactin in the blood. Diseases such as sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, aneurysm and head radiation may also be involved, as well as kidney failure, liver cirrhosis and hypothyroidism.
Prolactin test for men
In men prolactin values should be at most 20 ng / mL, and the higher that value, the greater the risk of a tumor called prolactinoma.
When observing this increase in the blood test the doctor can request imaging tests to better evaluate the gland. Tests that may also be requested are the X-ray of the head and MRI.
Treatment to lower prolactin
The treatment is indicated to combat infertility, sexual problems and strengthen bones. For this you may need to take medications such as Bromocriptine and Cabergoline (lisuride, pergolide, quinagolide).
Surgery is indicated to remove the tumor when it is large or increasing in size. Radiation therapy is not always indicated because the success rate is not very high.
The test should be repeated every 2 to 3 months in the first year of treatment, and then every 6 months or year by year, as the endocrinologist prefers.