There are two types of stroke: stroke, which is characterized by disruption of blood circulation in a certain area of the brain and hemorrhagic stroke characterized by rupture of a blood vessel which results in bleeding inside the skull.
These changes cause symptoms such as loss of strength or tenderness of a body region, dizziness, blurred vision or fainting, and should be treated quickly to avoid the risk of sequelae. To learn more about the main symptoms and treatment of stroke, see all about stroke.
In addition, each type of stroke also subdivides into other types, according to its cause and affected brain site. The main types are:
1. Ischemic stroke
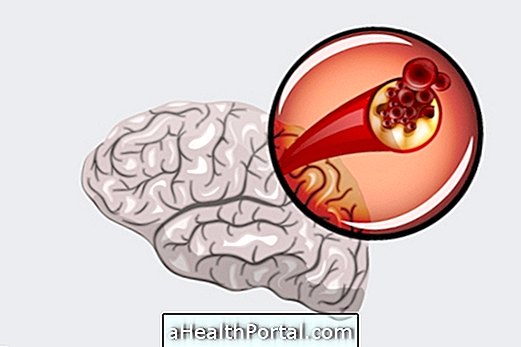
The cerebral ischemia that happens in this type of stroke can occur in 2 ways:
- Thrombosis : is the main cause of stroke, and it happens due to obstruction of blood flow in the vessel by fat plaques, called atherosclerosis, which occurs either in the small or large vessels of the brain.
Atherosclerosis of the vessel will form over the years, due to life habits and diseases without proper treatment such as obesity, smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol and triglycerides and diabetes.
- Embolism : A stroke by embolism occurs when a plaque of atherosclerosis or a clot detaches from another site of the body or heart, being carried by the bloodstream into the brain.
This is more common in people who have some cardiac arrhythmia, such as atrial fibrillation, heart murmurs, or some bad artery formation in the body, such as an aneurysm, for example, because in these cases there is a greater risk of clot formation.
- Other causes : Some of the less common causes of ischemic stroke are diseases that cause increased blood clotting, inflammation of the vessels, calcification or tumor in the heart, spasm of the cerebral vessels, or even the use of illicit drugs such as cocaine and amphetamine .
In some cases, transient ischemic stroke can occur, in which the symptoms last, usually, about 1 hour, and do not leave sequelae. This type can also be known with pre-stroke, so it is important to go to the emergency room to make an assessment and start appropriate treatment to prevent it from developing into a stroke.
Treatment of this type of stroke should be started early in the emergency, with medicines to improve circulation, such as AAS, and to control pressure, such as Captopril. To better understand how ischemic stroke treated, see how stroke treatment is done.
2. Hemorrhagic stroke

Hemorrhagic stroke can also happen in 2 ways:
- Intracerebral Hemorrhage: Bleeding that occurs within the brain due to rupture of a blood vessel, which may be small, or large, to the point of causing intense inflammation and swelling of the brain.
The main cause of intracerebral stroke is high blood pressure, but it can also be caused by degeneration of vessels due to age, use of illicit drugs such as cocaine and methamphetamine, blows to the head, rupture of an aneurysm, brain tumor or due to the use of anticoagulant medications, for example.
- Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Bleeding that occurs in the meninges, which are films that involve the brain, so they can compress the brain and cause symptoms.
The main causes of subarachnoid hemorrhage are the rupture of the aneurysm or severe blows to the head, which occur in situations of cranioencephalic trauma due to accidents. Find out what the symptoms, causes and possible sequelae of cerebral hemorrhage are.
Cerebral haemorrhage should be treated according to its cause, starting as soon as possible, to avoid complications and sequelae, and may be with pressure control, surgery, or adjustment of medications, for example. See also further details on the treatment and recovery of stroke types.