Tumor, neoplasia and cancer are ways to characterize tissue growth that happens incorrectly or exaggerated. This error can arise due to changes in the DNA of the cell, caused by hereditary causes or by exposure to risk factors such as radiation, infections by certain viruses or chemicals, for example.
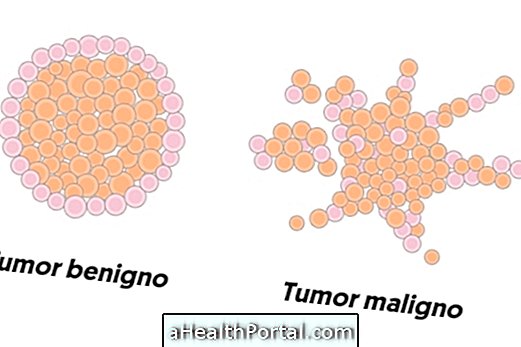
Tumor and cancer are forms of neoplasia. It is called a benign tumor when the proliferation of cells is organized, limited and slow, not causing great health risks. Already the malignant tumor, also called cancer, arises when the cells proliferate of uncontrolled form, aggressive and with capacity to invade neighboring organs.
Anyone can develop a neoplasia, however the risk usually increases with aging. Nowadays, most cases can be cured by medicine, even in cases of cancer, and in addition, it is known that many of the cases can be prevented by avoiding habits such as smoking, alcohol consumption or diet unbalanced, for example.
What is Neoplasm
The neoplasia encompasses all cases of exaggerated growth of a tissue, due to an incorrect proliferation of the cells, which may be benign or malignant. Normal cells that form the body's tissues are constantly multiplying, which is a normal process for development and survival, and each type of tissue has a suitable time for it, however, some stimulus may cause changes in its DNA that lead to defects in this process.
In practice, the term neoplasia is poorly used, and the terms "benign tumor", "malignant tumor", or "cancer" are more commonly used to determine its existence. Thus, every tumor and all cancer are forms of neoplasia.
Benign tumor
Tumor is the term used to report the existence of a "mass" that does not match the physiology of the organism and can arise anywhere in the body. In the case of the benign tumor, this growth is controlled, with cells that are normal or present only small changes, forming a localized, self-limited mass and of slow growth.
Rarely benign tumors are life-threatening, and are usually reversible when the stimulus that causes them is removed, either in the form of hyperplasia or metaplasia.
Classifications of benign tumor:
- Hyperplasia : characterized by the localized and limited increase of the cells of a tissue or organ of the body;
- Metaplasia : There is also localized and limited proliferation of normal cells, however, they are different from those of the original tissue. It works as a way of trying to repair the damaged tissue, as it can happen in the tissue of the bronchi due to the stimulus of the smoke or in the tissue of the esophagus, due to the reflux, for example
Some examples of benign tumors are fibroids, lipomas and adenomas.
2. Malignant tumor or cancer
Cancer is a malignant tumor. It arises when the cells of the affected tissue have a disorderly growth, which is usually aggressive, uncontrollable and rapid. This is because the multiplication of cancer cells does not follow the natural cycle, there is no death in the correct period, and persisting even after the withdrawal of the causative stimuli.
By having a more autonomous development, the cancer is able to invade neighboring tissues and to provoke metastases, besides being more difficult to treat. The disordered growth of cancer is capable of causing effects throughout the body, causing various symptoms and even death.
Classification of malignant tumor:
- Carcinoma in situ : it is the first stage of cancer, where it is still located in the tissue layer where they developed and there was no invasion to deeper layers;
- Invasive cancer : happens when cancer cells reach other layers of tissue where they arise, can reach neighboring organs or spread through the blood or lymphatic.
There are more than 100 types of cancer, since they can arise in any part of the body, and some of the most common are the breast, prostate, lung, intestine, cervix or skin, for example.

How to prevent
Many cases of neoplasia can be prevented, especially those that are related to smoking, such as lung cancer, or the consumption of alcoholic beverages, such as cancer of the esophagus and liver. In addition, it is known that a diet with excess red meat and fried foods may be related to the onset of certain types of tumor, such as colon, rectum, pancreas and prostate.
A diet rich in healthy foods like vegetables, grains, olive oil, nuts, almonds nuts can help prevent the development of many cancer cases. However, skin tumors can be avoided with protection against ultraviolet rays, with the use of sunscreen, hats and avoiding sun exposure in the hours of greater radiation, between 10 and 16 hours.
In addition, from time to time, specific tests are given for the screening and early detection of certain cancers, such as mammography for screening for breast cancer, rectal examination for prostate cancer, and colonoscopy for screening for colon cancer, for example.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment of neoplasms is done according to the type and extent of the disease. In general, antineoplastic drugs, such as chemotherapy, and radiotherapy treatments are used to destroy or limit tumor growth.
In many cases surgical procedures are also indicated to remove the tumor and facilitate the treatment or decrease the symptoms. Learn more about ways to treat cancer.
During the treatment of cancer, it is also very important to care for the patient in general, taking care also to reduce their suffering, especially in advanced cases, with the treatment of physical, psychological and social symptoms, also giving attention to the family. This care is called palliative care. Learn more about what palliative care is and how it is done.