The chances of having a cardiovascular disease, such as high blood pressure or heart failure, are higher with aging, being more common after age 60. This happens not only due to the natural aging of the body, which leads to decreased strength of the heart muscle and increased resistance in blood vessels, but also due to the presence of other problems such as diabetes or high cholesterol.
Thus, it is advised to go to the cardiologist annually and, if necessary, to have heart examinations from the age of 45 in order to detect early changes that can be treated before a more serious problem develops. See when to have a cardiovascular checkup.
1. High pressure

High blood pressure is the most common cardiovascular disease in the elderly, being diagnosed when blood pressure is above 140 x 90 mmHg in 3 consecutive evaluations. Understand how you can tell if you have high blood pressure.
This problem in most cases is caused by excessive salt intake in the diet associated with sedentary lifestyle and family history. In addition, people with a well-balanced diet can develop the disease due to aging vessels, which increase pressure on the heart and hamper cardiac contractility.
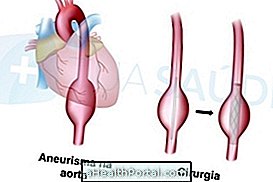
Although it rarely causes symptoms, high blood pressure needs to be controlled because it can cause other more serious problems, such as heart failure, aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, stroke, for example.
2. Heart Failure
The development of heart failure is often related to the presence of uncontrolled high blood pressure or other untreated heart diseases, which weaken the heart muscle and hamper the work of the heart, making it difficult to pump blood.
This heart disease usually causes symptoms such as progressive tiredness, swelling of the legs and feet, feeling of shortness of breath at bedtime and dry cough that often makes the individual wake up at night. Although there is no cure, heart failure should be treated to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. See how the treatment is done.
3. Ischemic heart disease
Ischemic heart disease arises when arteries that carry blood to the heart become clogged and fail to deliver enough oxygen to the heart muscle. In this way, the walls of the heart may have their contraction reduced totally or partially, which leads to the difficulty of cardiac pumping.
Heart disease is often more common when you have high cholesterol, but people with diabetes or hypothyroidism are also more likely to have the disease that causes symptoms such as constant chest pain, palpitations, and excessive tiredness after walking or climbing stairs.
This disease should always be treated by a cardiologist, avoiding the development of more serious complications such as decompensated heart failure, arrhythmias or even cardiac arrest.
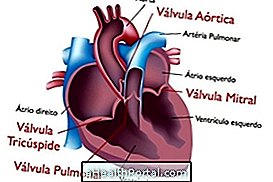
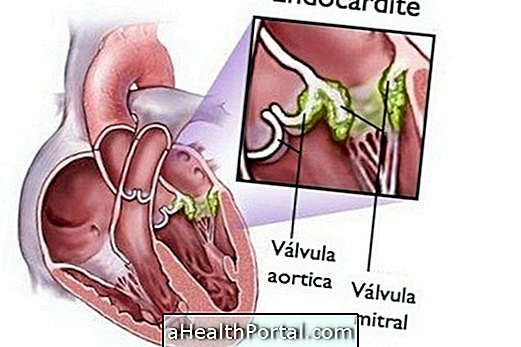
4. Valvopathy

With advancing age, men over age 65 and women over 75 years old are more likely to accumulate calcium in the valves of the heart that are responsible for controlling the passage of blood into and into the vessels of the body. When this happens, the valves thicken and harden, opening with greater difficulty and making it difficult to pass blood.
In these cases, the symptoms may be slow to appear. With the difficulty of passing blood, accumulation occurs, leading to dilation of the heart walls, and consequent loss of strength of the heart muscle, resulting in heart failure.
Thus, people over the age of 60, even if they do not have heart problems or symptoms, should have regular consultations with the cardiologist to evaluate the heart's functioning so as to detect problems that are silent or are not yet very advanced.
5. Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia can occur at any age, however, it is more common in the elderly due to the reduction of specific cells and the degeneration of the cells that drive the nerve impulses that cause the heart to contract. In this way, the heart may begin to contract irregularly or to beat less often, for example.
Normally, the arrhythmia does not cause symptoms and can only be identified after an electrocardiogram exam, for example. However, in more severe cases, symptoms such as constant tiredness, a sore throat or chest pain, for example. In these cases, it is recommended to take the treatment to relieve the symptoms.
Understand how cardiac arrhythmias are treated.