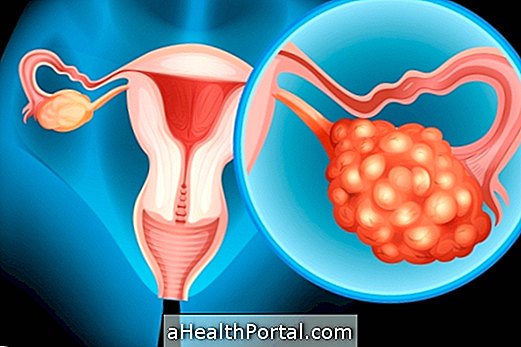
The uterine prolapse corresponds to the descent of the uterus into the vagina caused by the weakening of the muscles that keeps the organs inside the pelvis in the correct position, being thus considered the main cause of low uterus. Understand what the low uterus and main symptoms are.
Although it is more common in older women or who have had several normal births, this change may also occur before menopause or during pregnancy.
Uterine prolapse can be classified according to the level of descent of the uterus by the vagina in:
- Grade 1 uterine prolapse, in which the uterus descends, but the cervix does not appear on the vulva;
- Grade 2 uterine prolapse, in which the uterus descends and the cervix appears along with the anterior and posterior wall of the vagina;
- Uterine prolapse of grade 3, in which the uterus is outside the vulva up to 1 cm;
- Uterine prolapse grade 4, in which the uterus externalizes more than 1 cm.
Other organs of the pelvis region such as the walls of the vagina, bladder, and rectum may also undergo this displacement due to the weakening of the pelvic support muscles.
Pictures of uterine prolapse


Main symptoms
The main symptoms of uterine prolapse are:
- Stomach ache;
- Vaginal discharge;
- Sensation of something coming out of the vagina;
- Urinary incontinence;
- Difficulty evacuating;
- Pain in sexual intercourse.
When uterine prolapse is less severe the symptoms may not be observed. However, when signs and symptoms indicative of uterine prolapse are identified, it is important to consult a gynecologist to confirm the diagnosis and start treatment.
Uterine prolapse in pregnancy
Uterine prolapse in pregnancy is very rare and can occur before or during pregnancy. In addition, prolapse of the uterus in pregnancy can lead to cervical infection, urinary retention, miscarriage, and preterm labor. Therefore, all guidelines of the obstetrician should be followed to reduce the risk of complications.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of uterine prolapse is established according to the degree of descent of the uterus, and exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles, which are Kegel exercises, may be indicated. Here's how to do Kegel exercises.
In addition, the use of hormone-containing creams or rings to be applied to the vagina may help restore vaginal tissue, however, when it comes to severe uterine prolapse, surgery alone can be effective.
Surgery for uterine prolapse
Surgery for uterine prolapse is safe and effective and is indicated when recovery does not respond to other forms of treatment.
According to the doctor's indication, surgery can be done with the aim of:
- Repair the uterus: in these cases the surgeon restores the uterus to its place, keeping it inside the vagina through a device called pessary and, proceeds to the placement of prosthesis, called nets, that maintains the uterus in its position;
- Removal of the uterus: in this surgery partial or total withdrawal of the uterus occurs, and usually occurs in menopausal women, or when the prolapse is very severe. Hysterectomy is effective in curing uterine prolapse, but may trigger immediate menopause if the ovaries are removed. See what else can happen after the uterus is removed.
Learn how recovery from surgery for uterine prolapse is.
Causes of Uterine Prolapse
The most common cause of uterine prolapse is the weakening of the pelvis due to aging. However, other causes that contribute to the occurrence of prolapse may be:
- Multiple births;
- Menopause due to reduction of the estrogen hormone;
- Sequelae of previous infections in the pelvis region;
- Obesity;
- Excessive lifting of weights.
In addition to these causes, chronic cough, intestinal constipation, pelvic tumors and accumulation of fluid in the abdomen cause increased pressure in the abdomen and pelvis and therefore can also cause uterine prolapse.
The diagnosis of uterine prolapse is made with clinical examinations that evaluate all organs of the pelvis simultaneously, as well as gynecological exams such as colposcopy and vaginal smears made by gynecology to evaluate the best form of treatment. See which are the main exams requested by the gynecologist.