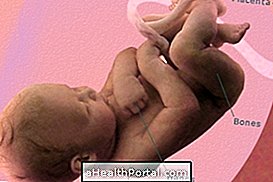
Cryopreservation serves to freeze embryonic stem cells that can be used to treat various diseases. The technique is to freeze these cells at very low negative temperatures, about -196 ° C, allowing them to be available anytime for 20 or 25 years for use by the baby or family.
This procedure is done right after birth and does not cause pain in the baby or the mother and the cells when necessary can be thawed and used in the treatment of more than 80 diseases, such as some types of leukemia, Hodgkin's disease and some types of anemias, for example.
Stem cells can also be known as stem cells, and are cells that can be transformed into several different types of cells, such as brain, blood, bone, or muscle cells, for example.
How is the collection of stem cells for cryopreservation
Collection of cryopreserved stem cells is done shortly after delivery, which are collected from the blood and umbilical cord tissue and collection does not involve risks or pain for the mother or the baby.
Cell cryopreservation can be done in a public bank through the BrasilCord Network program, where the cells are donated to society and can be used for the treatment of diseases or medical research or can be done in a private way for the personal use of the cell. family.
To do this, you should talk to your doctor and get the lab kit you need to collect at least 3 months before your due date. Cryopreservation is done by specialized laboratories such as HLA - Laboratory of Histocompatibility and Cryopreservation or Tommasi Laboratory, which have plans paid for the preservation of cells for 25 years.
What happens on the day of delivery
On the day of delivery, the parents must bring the kit from the laboratory to the hospital and should inform the medical staff that it is to collect blood or umbilical cord tissue. The kit provides the medical staff with all the necessary material to collect and transport the sample to the laboratory.

What diseases can stem cells treat
These cells can be used to treat more than 80 types of diseases, such as:
- Some types of Cancer such as Hodgkin's Disease, Myelofibrosis or some types of Leukemia;
- Blood diseases such as Beta thalassemia or Sickle cell anemia;
- Metabolism disorders such as Krabbe's disease, Gunther's disease or Gaucher's disease;
- Immunodeficiencies such as chronic granulomatous disease or Griscelli's syndrome;
- Marrow-related impairments such as some types of anemia, neutropenia or evanes syndrome;
- Osteopetrosis.
See more diseases in Stem Cell Treatment.
In addition, some research indicates that stem cells have the potential to be used in the treatment of diseases that have not yet been cured or effective treatments such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Cerebral Palsy, AIDS, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Type 1 Diabetes.
Advantages of Saving Stem Cells
Saving baby umbilical cord stem cells can be helpful in treating diseases that the baby or his or her direct family may have. Thus, the advantages of cryopreservation include:
- Protect the baby and the family : in case there is a need to transplant these cells to their conservation reduces the chances of rejection for the baby, and there may also be the possibility that these can be used to treat any direct family that may need, as a brother or cousin, for example.
- It allows the immediate availability of cells for transplantation in case of need;
- Method of simple and pain-free collection, done soon after birth and does not cause pain to the mother or baby.
The same cells can be obtained through the bone marrow, but the chances of finding a compatible donor are smaller, besides the procedure to collect the cells have risks, being necessary to perform a surgery.
Cryopreservation of stem cells during childbirth is a service that can be very costly and the decision whether or not to use this service should be discussed with the doctor so that recent parents can make the best decision for their baby.
In addition, stem cells serve not only to treat future illnesses that the baby may have, but can also serve to treat diseases of direct family members such as sibling, parent or cousin.