Raynaud's disease is characterized by a change in the blood circulation of the hands and feet, and may also reach the fingers, nose, and ear lobes. The color of the skin varies abruptly, becoming initially pale and cold, turning to bluish or purple and finally, the skin returns to its normal reddish color.
The cause of the sudden change in the color of these regions is unknown, but studies have shown that it may be associated with exposure to cold and sudden emotional changes and therefore this disease is more frequent among women. His first episode usually happens before he is 40 years old.

Main symptoms
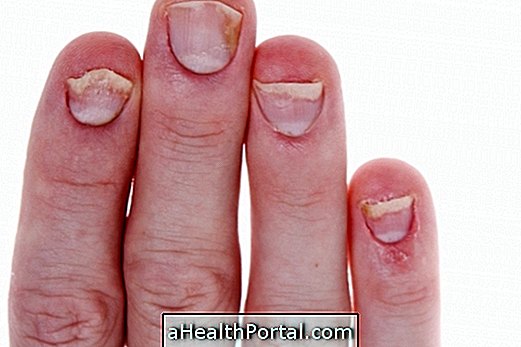
The symptoms of Raynaud's disease most often appear on colder days, when the person needs to get something in the freezer, or when it enters the sea and the water is very cold. In these cases, there is a change in the blood circulation of the extremities, like tips of the fingers, ears, nose and feet, for example.
Due to the low amount of blood that reaches the extremities, these regions become whitish and cold, and there may be a tingling sensation. Get to know other symptoms of the Raynaud phenomenon.
Causes of Raynaud's disease
The main cause of the Raynaud phenomenon is constant or prolonged exposure to cold, which results in altered blood flow. However, this phenomenon can also happen due to other situations, such as:
- Polyomyositis and dermatomyositis;
- Rheumatoid arthritis;
- Sjögren's Syndrome;
- Hypothyroidism;
- Carpal tunnel syndrome;
- Polycythemia vera;
- Cryoglobulinemia.
In addition, the Raynaud phenomenon can happen as a consequence of use of some medicine, cigarette use and performing activities with repetitive movements, for example.
How is the treatment done?
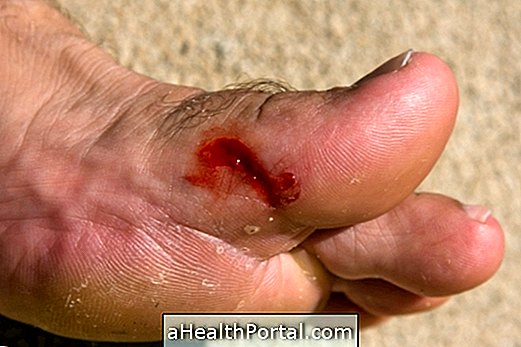
The Raynaud phenomenon usually does not require specific treatment, and it is only recommended, in most cases, that the region be heated so that the circulation is activated and restored. However, it is important to see a doctor if the symptoms persist or the extremities are dark, as it may mean that tissue death is due to lack of oxygen, and amputation of the affected region may be necessary.
To avoid necrosis, it is recommended to avoid cold places and wear gloves and thick socks in winter, for example. In addition, it is indicated not to smoke, because nicotine can also interfere in the blood circulation, reducing the amount of blood that reaches the extremities.
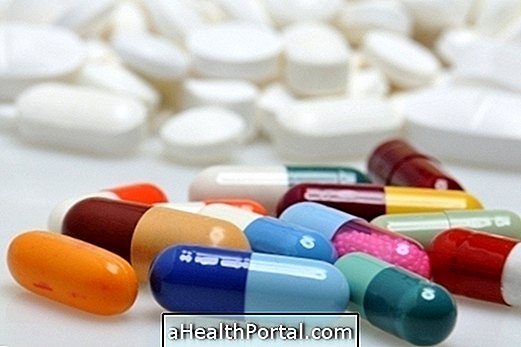
However, when the extremities are constantly cold and whitish, the doctor may recommend the use of some medicines, such as Nifedipine, Diltiazem, Prazosin or Nitroglycerin in ointment.