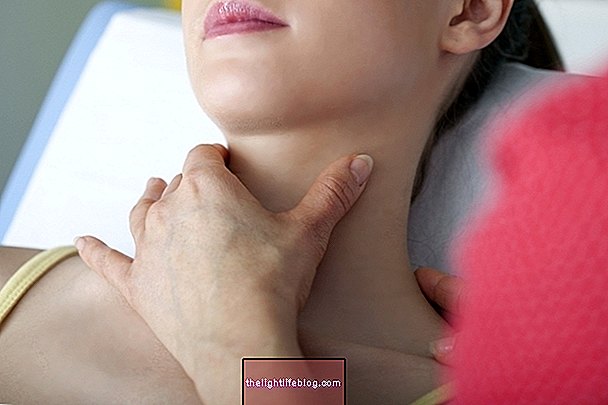
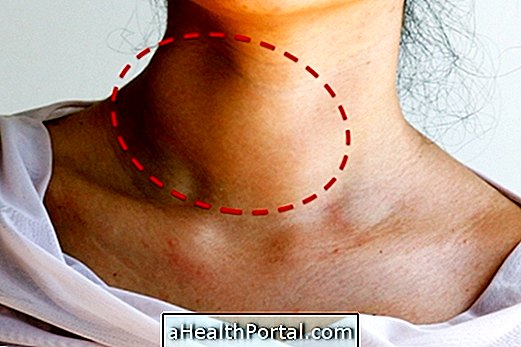
The goiter arises when the thyroid gland grows in size, forming a sort of lump or lump in the neck, which becomes rounder and wider than normal. Goitus usually can be easily observed without great difficulty, and it can be symmetrical, asymmetrical, composed of a nodule or a set of them, being in these cases known as nodular or multinodular goiter.
Goitre can have several causes, but it is common to develop disorders of thyroid function, such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. It is therefore recommended to consult an endocrinologist as soon as possible so that you can investigate and treat the problem.

Main Symptoms
The main symptoms that indicate the onset of goiter include:
- Difficulty swallowing;
- The appearance of a lump or lump in the neck;
- Coughing;
- Discomfort in the neck region;
- Feeling of shortness of breath;
- Hoarseness
In addition, symptoms such as easy tiredness, depression, muscle or joint pain that may indicate the presence of hypothyroidism may also arise.
Possible causes
Some of the possible causes that can lead to the onset of goiter include:
- Disorders of thyroid function such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism;
- Use of certain medications;
- Autoimmune diseases such as autoimmune thyroiditis;
- Infections;
- Thyroid tumor.
Goiter can also arise due to deficiencies in iodine, which cause the thyroid gland to be forced to work harder to capture iodide needed for the synthesis of thyroid hormones. This forced labor done by this gland leads to its enlargement and thus to the appearance of goiter. In addition, there are cases where goitre appears at birth, known in these cases as congenital goiter.
How to know if I have goitre
The diagnosis of goiter can be made through a set of tests, which determine if goiter is malignant or not, whether or not cancer.

Firstly, the doctor begins by observing the presence of a lump in the neck, usually asking for an ultrasound or ultrasound that will allow a better visualization of the thyroid gland. In addition, the diagnosis is also complemented by specific blood tests that evaluate the amount of thyroid hormones in the blood, such as T4, T3 and TSH, which allows to identify if there are disturbances in thyroid function.
In cases where the doctor suspects thyroid cancer, he or she will recommend performing a biopsy or thyroid biopsy in which a small piece of the thyroid gland is removed. This test does not hurt and leaves no scar and the small piece collected is then smoothed in the laboratory.
Treatment
When goitre is caused by deficiencies in iodine, its treatment is done by administering iodine at doses 10 times higher than the recommended daily dose for a few weeks. With this treatment, the thyroid gland can effortlessly capture the iodide it needs for the synthesis of hormones, which after a few weeks can bring it back to normal size. However, in more severe cases it may be necessary to maintain the treatment for life.
In cases of disorders of thyroid function such as hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism the treatment is not linear and can be done using medicines such as Tapazole or Puran T4 or with radioactive iodine capsules. In cases of thyroid cancer, it may be necessary to remove this gland through surgery.
How to prevent the onset of goiter
The emergence of goitre that originates in deficiencies in iodine can be prevented through the consumption of foods rich in this mineral, such as:
- Mackerel, Mussel, Hake;
- Iodized salt, Salmon, Shrimp;
- Tuna, Kidney, Milk;
- Eggs, Beer.
For the most part, iodine-rich foods are marine in origin, so fish and seafood are the richest choices in iodine that should be regularly consumed to prevent Iodine deficiency-related diseases such as goiters. Learn more about what foods rich in iodine and what diseases can be caused by your lack by clicking here.