The surgery for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome consists of making a cut between the palm of the hand and the wrist to release the nerve that is being pressed and causing symptoms such as tingling or stinging sensation in the hand and fingers.
Carpal tunnel decompression surgery is generally recommended in cases where remedies and physiotherapy sessions have had little or no improvement and in cases where there is a large nerve compression.
The surgery is done by an orthopedist, is relatively simple and, in most cases, provides a complete and permanent cure. However, as with any type of surgery there is always a small risk of complications such as nerve damage or infection, for example.

How Carpal Tunnel Surgery Is Performed
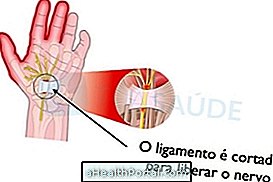
Carpal tunnel surgery consists of making a small opening between the palm of the hand and the wrist to cut the ligament that presses the nerve to relieve the pressure on it. The surgery can be done with two different techniques:
- Traditional technique: The surgeon makes a large cut in the palm of the hand over the carpal tunnel and cuts the ligament to release the nerve;
- Laparoscopy technique: The surgeon uses a device with a small camera attached to see the inside of the carpal tunnel and cuts the ligament through one or two small cuts on the hand or wrist.
Anesthesia for carpal tunnel surgery can be done on the hand, near the shoulder or the surgeon can opt for general anesthesia. However, whatever the anesthesia, the patient feels nothing during the surgery.
Risks of carpal tunnel surgery
Carpal tunnel surgery, like all surgeries, has some risks such as infection, bleeding, nerve damage, and persistent wrist or arm pain. In addition, after surgery for decompression of the carpal tunnel, symptoms such as tingling and feeling of needles in the hand may return.
How is recovery from surgery?
The recovery time after carpal tunnel surgery depends on the type of technique used, and the recovery time for traditional surgery is generally somewhat longer than the recovery time for laparoscopic surgery. In general, people who work in offices and have to be typing need to stay away from work for 10 days.
However, regardless of the technique used, in the postoperative period of carpal tunnel surgery the patient should:
- Rest at rest and take Paracetamol or Ibuprofen for relief of pain and discomfort;
- Use a splint to immobilize the wrist to avoid damage caused by joint movement for 8 to 10 days;
- Keep the operated hand lifted for 48 hours to help reduce any swelling and stiffness in the fingers;
- After removing the splint an ice pack can be placed in place for pain relief and swelling reduction.
After surgery, you may feel pain or weakness that can take a few weeks to months to pass and a doctor indicates when the patient can use the hand to do light activities that do not cause pain or discomfort and when you can return to work.
After the surgery, it is usually necessary to do a few more sessions of physical therapy for the carpal tunnel and exercises to prevent the surgery scars from sticking and preventing the free movement of the affected nerve. Here are some examples of exercises in: Treatment for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Check out other tips in the following video: