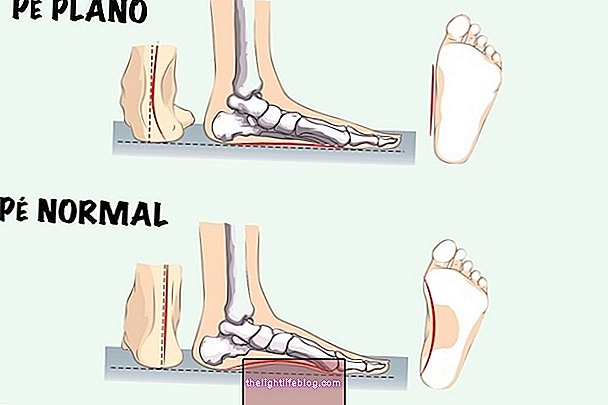
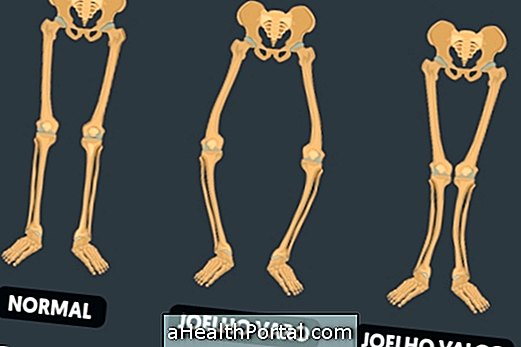
Valgus knee or valgus is a misalignment of the hip and legs that causes the knees to be turned inwards and feet out. This condition is popularly known as X-shaped legs or scissors.
The knee valgus can easily be noticed simply by observing that the knees can touch, but the ankles are distant, which can cause symptoms such as pain and lack of stability in the knee.
Symptoms of valgus knee
Usually the person with knee valgus feels pain inside or outside the knee, hip, foot or leg, and lack of stability in the knee.
If it is not corrected, the person can develop arthrosis, for example, which is a degeneration and looseness of the joints. Learn what arthritis is and how to avoid it.
What is the difference for varus knee
While in the knee valgus the knees are rotated inward and the feet out, in the varus knee the legs are arched, as if the person were ready to mount on a horse.
The varus knee is rarer than the knee valgus and usually occurs because of rickets, which is a disease characterized by vitamin D deficiency that leaves the bones more fragile due to insufficient mineralization, or because of genetic changes that are only perceived at birth and throughout the development of the child.
Both conditions may occur at birth and be corrected throughout development. Understand better what is the varus knee and how to treat.
Main causes
Valgus knee is usually seen in women because they have a wider hip compared to men and weaker leg muscles. In addition, other causes of valgus knee are:
- Malformation and development of the legs;
- Ankle stiffness;
- Poorly executed physical exercises such as squats;
- Genetic factors;
- Diseases, such as scurvy and rickets, in which vitamin deficiency leads to weakness in the bones.
Normally children are born with valgus or varus knee, but this is corrected throughout the growth. If there is no correction, the valgus knee may favor the occurrence of sprains, arthrosis, tendinitis and bursitis. Understand the difference between tendinitis and bursitis and how to treat it.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment to correct the valgus knee is made by appointment of a physiotherapist and aims to strengthen the muscles and decrease the stiffness of the joint by means of corrective exercises. In addition, the use of orthopedic insoles can be indicated by the physiotherapist, as they promote the realignment of the ankle and feet and, consequently, prevent knee misalignment.
It is also advisable to avoid some types of exercise, such as races and squats, as they can increase pain, and decrease the intensity and rhythm of physical activities. However, you should take into account the profile of the person who has knee valgus, because if you are overweight, you should lose weight so that the pain decreases and the chances of knee realignment increase. The exercises should always be followed by a professional.
Surgical treatment only occurs when there is a very large degree of misalignment that physical therapy alone can not correct. After surgery, physiotherapy sessions should be performed to make recovery more rapid and effective.