The treatment for bursitis, which consists of inflammation of the bursa, which is a pouch used to protect the joint and bone, should be guided by an orthopedic physician and physiotherapist and is intended to relieve the pain and inflammation of the affected region.
Medications may initially be used, but physical therapy sessions may be used to control symptoms, but in the latter case, surgery to drain the fluid from the bursa or completely remove the bursa may also be a treatment option, but only in cases where there is infection and the other treatments have no effect.
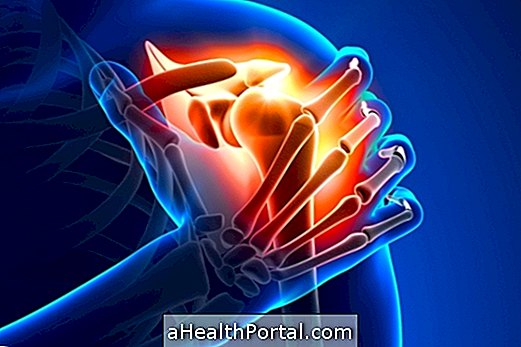
What is bursitis?
Bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa, which is a type of 'pouch' found within some joints that serves to protect and prevent friction between two bone ends. Some joints that contain the bursa, and which therefore can develop a bursitis are: the shoulder, hip, ankle, knee and heel.
In the shoulder there are two different bursae, the subacromial bursa and the subdelhotoid bursa and when they inflame they cause intense pain located at an exact point of the shoulder. These are the most common types because jobs like raising your arms to clean the windows or paint a wall can cause inflammation. See more about shoulder bursitis.
The following are the forms of treatments that can be used to treat bursitis.
Bursitis Remedies
Ingestion of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs, such as Dipyrone, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide or Diclofenac, may be doctor-directed. Diclofenac, Cataflan or Remon gel ointments, for example, are good options for topical medications. To use just apply a thin layer on the sore joint, 2 to 3 times a day.
These medications can be used daily for pain relief, but when pain and discomfort do not subside within 3 months, even with physical therapy, the orthopedist may indicate the use of corticosteroid injections.
In addition, antibiotics may be used when infection occurs, but this is very rare.
How is physiotherapy for bursitis?
Physical therapy for bursitis should be daily and consists of the use of analgesic and anti-inflammatory devices, such as Tens, ultrasound, galvanic current or microcurrent, for example to decrease the inflammation and pain of the affected region.
In addition, physical therapy also uses techniques and exercises to increase mobility of the affected joint and muscle stretches to improve its function. Other strategies that may also be useful are:
- Rest and
- Place an ice pack in the affected region for 20 minutes, about 3 times a day.
Physical therapy usually takes 6 months and after physical therapy, it is recommended that the individual continues to practice some physical activity to keep the joint hydrated and muscles strong, to avoid a new bursitis.
Home treatment to relieve symptoms
The home treatment consists of taking some care to relieve the pain and inflammation of the affected region, such as:
- Place ice for 20 minutes, about 3 times a day;
- Wear jewelry in case of bursitis in the knee, to support the joint and decrease the pain;
- Do not sleep to the hip side with bursitis;
- When sleeping, put pillows to support the joint.
In addition, as an alternative treatment to acupuncture, it can be a good option, because by applying the needles in the affected region or the corresponding meridian it is possible to reduce inflammation and pain.
Natural treatment for bursitis
Natural treatment can be done through food, increasing the consumption of foods with anti-inflammatory properties, with the aim of reducing inflammation and pain. See the following video:

Signs of improvement
Signs of improvement of bursitis arise with treatment and include reduction of pain in the affected region and difficulty in moving the affected limb.
Signs of worsening
Signs of worsening bursitis are related to its complications such as infection of the bursa, for example, and include increased pain in the affected region and difficulty in moving the limb, as well as redness and increased swelling of the affected region, which can get hot too.