Most cases of periodontitis have a cure, but their treatment varies according to the degree of evolution of the disease, and can be done through surgery or less invasive techniques, such as curettage, root planing or use of antibiotics, for example.
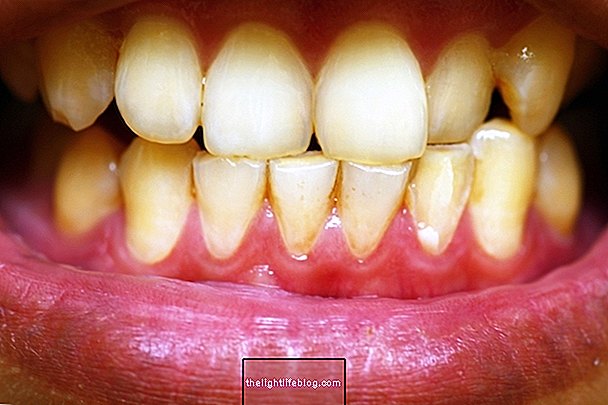
In addition, because periodontitis is caused by poor oral hygiene, which allows the growth of tartar and bacteria, it is important to brush the teeth at least 2 times a day, to use dental floss, to avoid cigarette smoking, and to make annual dentist.

Main treatments without surgery
Different treatment techniques that do not require surgery are usually used in milder cases of periodontitis and include:
1. Curettage
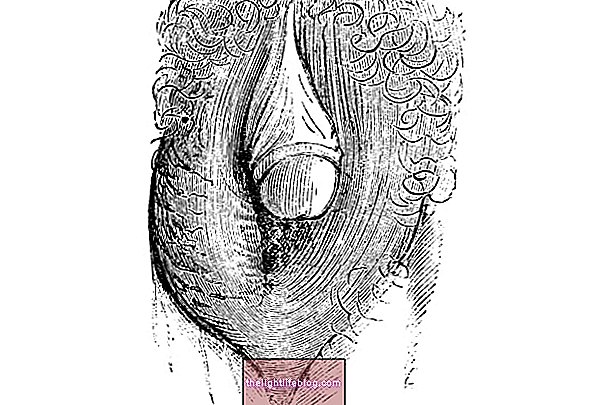
This technique is a type of deep cleansing of the teeth that allows to remove the excess of tartar and bacteria from the surface of the teeth and the interior of the gums, avoiding the appearance of infections that can affect the bones that hold the teeth.
Curettage is done by a periodontist or dentist, using special instruments in the office and, in some cases, can also be done with a laser.
2. Root planing
Flattening consists of smoothing the surface of the root of the teeth to reduce the chances that the bacteria will stick and develop, relieving inflammation of the gums and avoiding the worsening of periodontitis lesions.
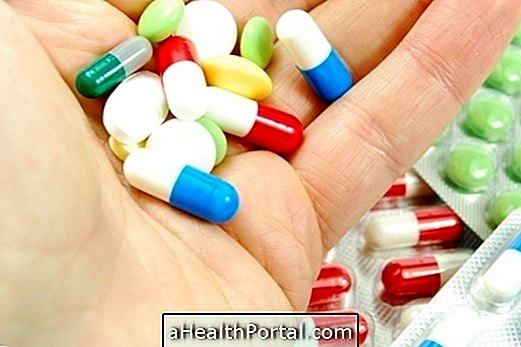
3. Antibiotics
Antibiotics, such as Amoxicillin or Clindamycin, eliminate and help control the growth of bacteria in the mouth and can be used as a tablet or as a mouthwash. They are usually used after curettage to keep teeth clean and ensure that all bacteria have been eliminated.
This type of medication should only be used with advice from the doctor and during the recommended period, as its excessive use can cause several side effects such as diarrhea, vomiting or recurrent infections.
Main types of surgery
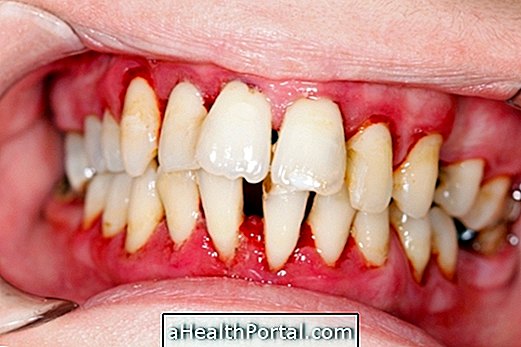
When periodontitis is in a more advanced stage and there are lesions on the gums, teeth or bones, it may be necessary to resort to some type of surgery such as:
- Depth Scaling : A part of the gum is lifted and exposed to the root of the tooth, allowing a deeper cleaning of the teeth;
- Gum graft : it is done when the gum was destroyed by the infection and the root of the teeth was exposed. Usually, the doctor removes a piece of tissue from the roof of the mouth and places it on the gums;
- Bone graft : This surgery is used when the bone has been destroyed and allows to keep the teeth safer. The graft is usually made with synthetic or natural material, being removed from another bone of the body or from a donor, for example.
These types of surgery are usually done at the dentist's office with local anesthesia and so it is possible to return home the same day, so there is no need to stay in the hospital.
The most important care after surgery is to maintain proper mouth hygiene and avoid hard foods the first week to allow the gums to heal. Here are some examples of what you can eat during this time.