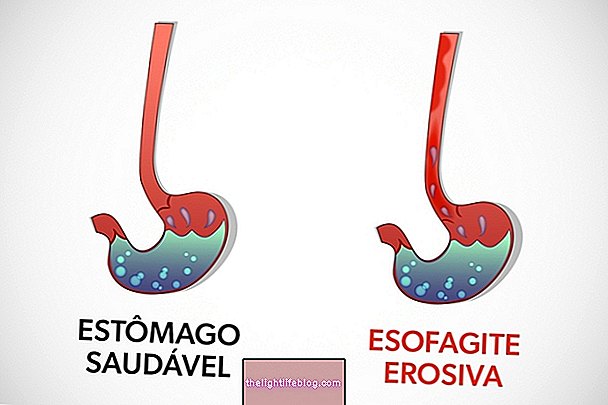
Acute alcoholic hepatitis is a type of hepatitis caused by excessive intake of alcoholic beverages, which cause the onset of symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting and loss of appetite, for example.
Generally, alcoholic hepatitis does not catch as it is not contagious. However, patients with hepatitis C, a type of hepatitis that passes through the blood, are at increased risk of developing alcoholic hepatitis if they drink too much alcohol.
Acute alcoholic hepatitis usually heals as long as the patient stops drinking alcohol and treats with medications prescribed by the hepatologist in order to avoid serious complications such as cirrhosis or liver failure. Learn all about cirrhosis here.
Symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis
Symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis may include:
- Abdominal pain on the right side;
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Swelling of the body, especially in the belly;
- Loss of appetite;
- Excessive tiredness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Loss of weight without apparent cause.
Typically, patients with symptoms and signs of alcoholic hepatitis who do not initiate appropriate treatment have a survival rate of about 6 months after the onset of the first symptoms. It is therefore very important to consult the hepatologist as soon as possible whenever symptoms of liver problems appear.
Diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis
The diagnosis of alcoholic hepatitis is made by a hepatologist through laboratory tests, such as ultrasonography or blood test to evaluate the levels of albumin and bilirubin, for example, as well as analysis of the patient's history, which usually includes excessive use of alcoholic beverages.
Treatment for alcoholic hepatitis
Treatment for alcoholic hepatitis should be directed by a hepatologist, but usually begins with the elimination of alcohol consumption and the use of drugs such as Ursodeoxycholic acid or Phosphatidylcholine, which reduce inflammation of the liver and relieve symptoms of hepatitis.
In addition, due to lack of appetite, it is common for patients with alcoholic hepatitis to malnutrition, so it is important to consult a nutritionist to make a proper diet or start eating food supplements, for example. See the video below for some recommendations:

In more severe cases, where there are large liver lesions, such as cirrhosis, the doctor may recommend doing a liver transplant to increase the chances of a patient's healing.