Ear, nose and throat surgery is performed on children, usually between the ages of 2 and 6 years, by the otorhinolaryngologist with general anesthesia when the child snores, has difficulty breathing, has repetitive otitis with hearing impairment.
The surgery takes about 20 to 30 minutes and the child may need to be hospitalized for one night for observation. Recovery is usually quick and simple, and in the first 3 to 5 days the child should eat cold food. From the 7th day, the child can go back to school and eat normally.
Indications for ear, nose and throat surgery
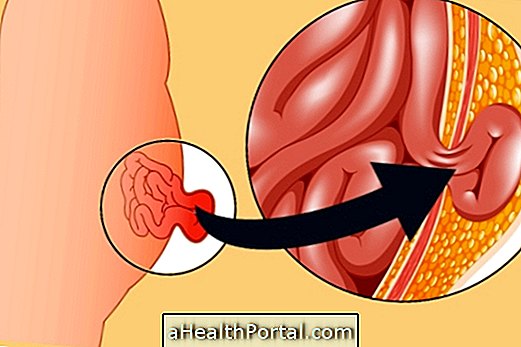
This ear, nose and throat surgery is indicated when the child has difficulty breathing and snores due to the growth of the tonsils and adenoids and gets a kind of ear secretion (otitis serosa) that impairs hearing.
The growth of these structures usually occurs after a viral infection in the child, such as chickenpox or influenza and when they do not reduce again, the tonsils in the throat and the adenoids, which are a kind of spongy meat that are located inside the nose, prevent the normal passage of the air and increasing the humidity inside the ears provoking an accumulation of secretion that can lead to deafness if not treated.
This obstruction usually causes snoring and sleep apnea which is respiratory arrest during sleep, putting the child's life at risk. Usually enlargement of the tonsils and adenoids regress to 6 years of age, but in these cases, which are common between 2 and 3 years, ear, nose and throat surgery is indicated at these ages.
The symptoms of fluid accumulation in the ear are very discrete and the otorrino needs to take called audiometry to decide to have surgery to measure if the child's hearing ability is at risk. Therefore, if the child:
- You have regular ear pain;
- You watch television very close to the set;
- Not responding to any sound stimulus;
- To be very irritated constantly
All these symptoms may be related to the accumulation of secretion in the ear, which may also reflect in difficulty of concentration and learning deficit.
Know what the audiometry exam consists of.
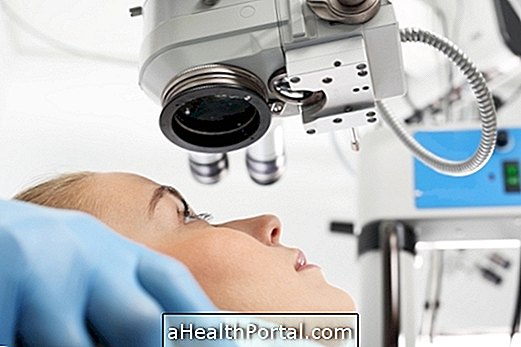
How is ear, nose and throat surgery done?
Ear, nose and throat surgery is done simply. The removal of the adenoids and tonsils is done by the mouth and nostrils, without the need for cuts on the skin. It is also introduced a tube, called ventilation tube in the inner ear with general anesthesia to air the ear and drain the secretion, which is removed within 12 months after surgery.
Recovery after ear, nose and throat surgery
Recovery after ear, nose and throat surgery is simple and quick, about 3 to 5 days in most cases. Upon waking up and for the first 3 days after surgery it is normal for the child to still breathe through the mouth, which can dry the operated mucosa and cause some pain and discomfort, and at this stage it is important to provide cold fluids to the child often.
During the week following surgery, the child should rest and not go to crowded places such as malls or even go to school to avoid infections and ensure a good recovery.
The food gradually returns to normal, according to the tolerance and recovery of each child should be given preference to cold foods and pasty consistency, which are easier to swallow like porridge, ice cream, pudding, gelatin, soup. At the end of 7 days, the food returns to normal, healing must be completed and the child can return to school.
Until the ear tube comes out, the child should wear earplugs in the pool and in the sea to prevent water from entering the ear causing an infection. During the bath, a tip is to put a small piece of cotton in the ear of the child and to pass moisturizing cream on top, because the fat of the cream will hinder the entrance of the water in the ear.
Useful links:
- Adenoid surgery
- Tonsillitis surgery