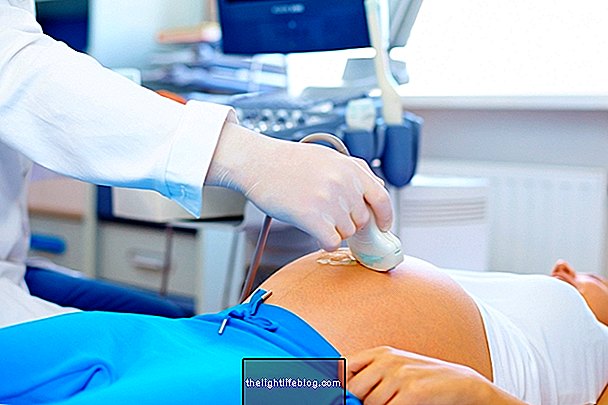
A woman with autoimmune hepatitis can become pregnant and have a successful pregnancy, provided that she is regularly accompanied by her obstetrician and hepatologist to avoid complications such as hemorrhage or rejection of the baby, for example.
Generally, autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy does not require treatment, but if it is necessary to take the autoimmune hepatitis medicines every day can and should only be used under the guidance of the hepatologist.
Autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy has no cure, but during this time the woman may feel symptom relief because the disease tends to develop more slowly.
Symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy are the same as those of the disease outside of this period and include:
- Excessive tiredness;
- Muscle pain and weakness;
- Loss of appetite;
- Abdominal pain;
- Skin and yellow eyes;
- Itching in the joints;
- Exaggerated increase of belly, for gestational age.
The symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis may vary according to the stage of development of the disease, however, during pregnancy the symptoms tend to be milder.
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis in gestation can be done at home with the ingestion of steroid medicines prescribed by the hepatologist, such as Prednisone, which reduces inflammation of the liver and keeps it controlled during pregnancy.
However, in some cases, autoimmune hepatitis in pregnancy may develop more slowly and cause few significant damage, so the doctor may recommend that the mother stop taking the medicines because they are not having a significant result . In such cases it is recommended to have regular visits to the obstetrician and hepatologist.
Autoimmune hepatitis usually does not pass from the mother to the baby and so there is no need for any special treatment during pregnancy.
Learn more about this disease in:
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Diet for autoimmune hepatitis