Internal bleeds are bleeds that occur inside the body and may not be perceived and are therefore more difficult to diagnose. These bleeds can be caused by injuries or fractures, but can also occur due to diseases such as hemophilia, gastritis or Crohn's disease, for example.
Treatment is usually performed through surgery, however, in some cases internal bleeding can stop on its own.

Most Common Symptoms
Symptoms that may occur during an internal bleeding depend on where it occurs and the severity of the injury. When blood contacts the tissues and internal organs it can cause pain and inflammation, and it may be easier to detect the affected site.
The most frequent symptoms that may be associated with internal bleeding at various sites are dizziness, weakness on one side of the body, fainting, decreased blood pressure, vision problems, severe headache, abdominal pain, difficulty swallowing and breathing, chest pain, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea and loss of balance and consciousness.
Possible causes
There are several causes that may be at the origin of an internal hemorrhage:
1. Injuries
Injuries caused by car accidents, aggressions or falls, for example, can damage the head, some organs, blood vessels or bones and cause internal bleeding.
2. Fracture
The bleeding can occur due to fractures in the bones, because they contain inside the bone marrow, which is where the blood is produced. The fracture of a large bone, such as the femur, for example can lead to the loss of almost half a liter of blood.
3. Pregnancy
Although not normal, bleeding may occur during pregnancy, especially in the first trimester, which may be a sign of miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy. Learn about the symptoms that may indicate ectopic pregnancy.
If bleeding occurs after 20 weeks of gestation, it may be a sign of a previous placenta, which runs when the placenta partially or fully recovers the opening of the cervix, and may cause symptoms such as severe vaginal bleeding. See what to do if that happens.
4. Surgery
During surgery it may be necessary to perform cuts to certain areas of the body that cause bleeding, which is controlled by the surgeon before the end of the procedure. However, there may be internal bleeding hours or even days after surgery, and it may be necessary to return to the hospital to stop bleeding.
5. Spontaneous bleeding
Internal bleeding may also occur spontaneously, especially in people taking anticoagulant medications or having some blood disorder.
6. Medications
Some medications, such as anticoagulants, can cause internal bleeding more easily after injury, as they prevent clotting.
In addition, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can cause bleeding into the gastrointestinal tract, especially in the esophagus, stomach and duodenum due to its side effects. This is because these drugs inhibit an enzyme in the stomach, responsible for the production of prostaglandins that act in their protection.
7. Alcohol abuse
Alcohol in the long run and in the long term can cause bleeding due to changes in clotting mechanisms and damage to the stomach. In addition, it can also cause liver cirrhosis which can lead to bleeding in the esophagus. See more symptoms caused by cirrhosis of the liver.
8. Insufficient coagulation factors
A healthy organism produces important clotting factors to staunch bleeding when an injury occurs. However, in some diseases such as hemophilia, these coagulation factors may be diminished or even absent, with a higher risk of bleeding. Learn more about this disease.
9. Chronic high blood pressure
In people whose blood pressure is generally high, weakening of the walls of some vessels can lead to aneurysms that can rupture and bleed.
10. Gastrointestinal disorders
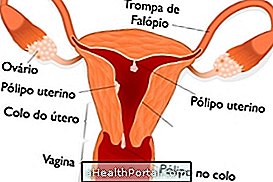
Gastrointestinal disorders such as intestinal polyps, stomach ulcers, colitis, Crohn's disease, gastroenteritis or esophagitis may also cause bleeding in the stomach or abdomen. Hemorrhages in the gastrointestinal tract are usually detected in the vomit or stool due to the presence of blood.

How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of an internal hemorrhage can be made in several ways, since it depends on many factors. It is usually done through a physical examination and blood tests in order to understand the severity of the bleeding and in cases where the bleeding is caused by an accident or a serious injury imaging can be performed at the site where bleeding is suspected.
Thus, an X-ray can be performed that can analyze the bones and detect fractures, or a CT scan where it is possible to analyze not only the bones, but also the tissues and blood vessels.
Other options include ultrasound, stool examination, endoscopy, colonoscopy, or angiography, which can also be used to detect a damaged artery.
What is the treatment
The treatment of internal bleeding depends on the cause, extent of bleeding, the organ, tissue or vessel that is reached and the state of health of the person.
Some internal bleeding can stop on its own without treatment. However, there are cases where surgery is urgently needed.