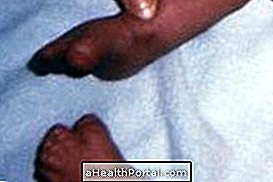
One of the ways to be suspicious if the child has cystic fibrosis is to observe if his sweat is saltier than normal, however the diagnosis of this disease is done through the test of the foot, which must be performed in the first month of life. In case of a positive result, the diagnosis is confirmed through the sweat test.
Cystic fibrosis is a hereditary disease without cure, in which some glands produce abnormal secretions that affect mainly the digestive and respiratory tract. Your treatment involves medicines, diet, physical therapy and, in some cases, surgery. Patients' life expectancy is increasing due to advances in treatment and the higher rate of adherence, and the person can reach the age of 40 on average.
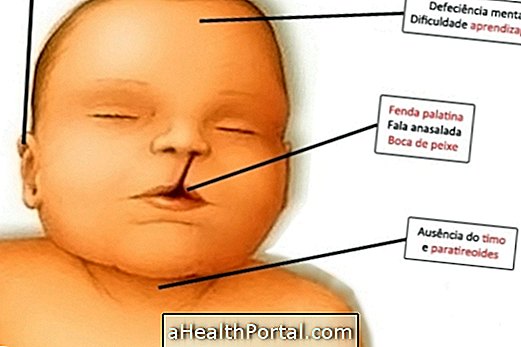
Symptoms of cystic fibrosis
The first sign of cystic fibrosis is when the baby can not eliminate meconium, the first stool of the newborn, on the first or second day of life. Sometimes drug treatment can not dissolve these feces, and they need to be removed through surgery. Other symptoms of this disease are:
- Salty sweat;
- Persistent chronic cough, disrupting food and sleep;
- Thick chondroleum;
- Recurrent bronchiolitis, which is the constant inflammation of the bronchi;
- Respiratory tract infections that recur, such as pneumonia;
- Difficulty breathing;
- Tiredness;
- Chronic diarrhea or severe constipation;
- Loss of appetite;
- Gases;
- Greasy, pale-colored stools;
- Difficulty gaining weight and belated growth.
These symptoms begin to appear in the first few weeks of life and the child should receive appropriate treatment to avoid worsening of the condition. However, cystic fibrosis may be mild in degree and symptoms may only manifest in adolescence or adulthood.


Diagnosis of cystic fibrosis
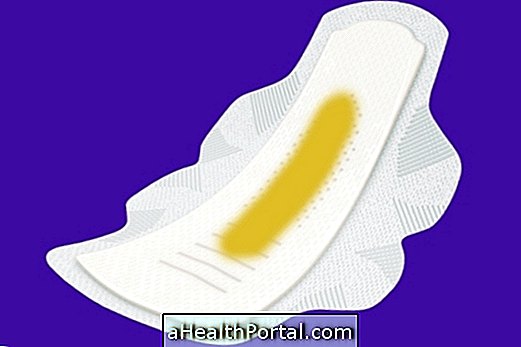
The diagnosis of cystic fibrosis is done through the baby's foot test, which is mandatory for newborns, and to have a reliable result, it is important that the baby is taken to the test before 30 days of age. In cases of positive result, the sweat test is then performed to confirm the diagnosis. In this test, a little baby sweat is collected and evaluated, because some changes in sweat indicate the presence of cystic fibrosis.
Even with the positive result of the 2 tests, the sweat test is usually repeated to be sure of the final diagnosis, and it is important to observe the symptoms presented by the baby. Older children who have symptoms of cystic fibrosis should have a sweat test to confirm the diagnosis.
In addition, it is important to perform a genetic test to check the mutation related to cystic fibrosis that the baby has, because depending on the mutation the disease may have a milder or more severe progression and may indicate the best treatment strategy that should be established by the pediatrician.
See other problems that can be identified in this test in: Diseases detected by the test of the foot.
Treatment of cystic fibrosis
Treatment for cystic fibrosis should start as soon as the diagnosis is made, even if there are no symptoms, since the goals are to delay lung infections and prevent malnutrition and delayed growth. In the treatment are used several remedies like:
- Antibiotics: avoid and treat infections by bacteria;
- Anti-inflammatory;
- Bronchodilators: facilitate breathing;
- Mucolytics: help thin the phlegm;
- Digestive enzymes: help digest food
- Supplement of vitamins A, E, K and D.
The treatment involves several professionals, because in addition to the use of medicines, it is also necessary to do respiratory physiotherapy, nutritional and psychological monitoring, oxygen therapy to improve breathing and, in some cases, surgery to improve lung function or lung transplantation. Here's how feeding can help treat this disease in: feeding for cystic fibrosis.
In Brazil there are several associations for parents who have children with cystic fibrosis, who bring information about the disease and how to live better with it. Family support and knowledge is essential for a better treatment outcome.
Complications of cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis causes complications in various organs of the body, which can cause:
- Chronic bronchitis, which is usually difficult to control;
- Pancreatic insufficiency, which can lead to malabsorption of ingested foods and malnutrition;
- Diabetes;
- Liver diseases such as inflammation and cirrhosis;
- Sterility;
- Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome (GAD), where a blockage of the intestine occurs, causing cramps, pain and swelling in the belly;
- Gall stones;
- Bone disease, leading to greater ease of bone fractures;
- Malnutrition.
Some complications of cystic fibrosis are difficult to control, but early treatment is the best way to increase quality of life and promote proper growth of the child. Although they have many problems, people with cystic fibrosis usually get to go to school and work.
Life expectancy
The life expectancy of people with cystic fibrosis varies from person to person according to mutation, sex, adherence to treatment, disease severity, age of diagnosis and clinical respiratory, digestive and pancreatic manifestations. The prognosis is usually worse for people who are not treated properly, have a late diagnosis or who have pancreatic insufficiency.
In people who have been diagnosed early, preferably soon after birth, it is possible for the person to reach the age of 40, but for this it is necessary to perform the treatment in the correct way. Learn how to treat cystic fibrosis.
Currently, about 75% of people who follow cystic fibrosis as recommended go through their teens and about 50% go through to the third decade of life, which was only 10%.
Even if the treatment is done correctly, unfortunately it is difficult for the person diagnosed with cystic fibrosis to reach age 70, for example. This is because even with adequate treatment, there is progressive impairment of the organs, which makes them fragile, weak and lose their function over the years, resulting, in most cases, in respiratory failure.
In addition, micro-organism infections are very common in people with cystic fibrosis and constant treatment with antimicrobials may cause the bacteria to become resistant and may further complicate the patient's clinical condition.