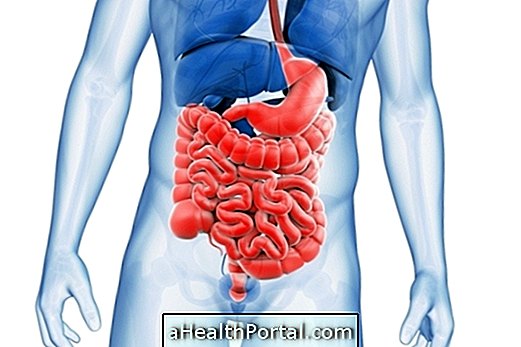
Polycythemia corresponds to an increase in the amount of red blood cells or erythrocytes in the blood, that is, above 5.4 million red blood cells in women and over 5.9 million red blood cells per μL in men.
Due to the increase in the number of red blood cells, the blood becomes more viscous, which causes the blood to circulate with more difficulty through the veins, which can cause some symptoms, such as headache, dizziness and even heart attack.
Polycythemia can be treated not only to decrease the amount of red blood cells and blood viscosity but also to relieve symptoms and prevent complications such as stroke and pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms of Polycythemia
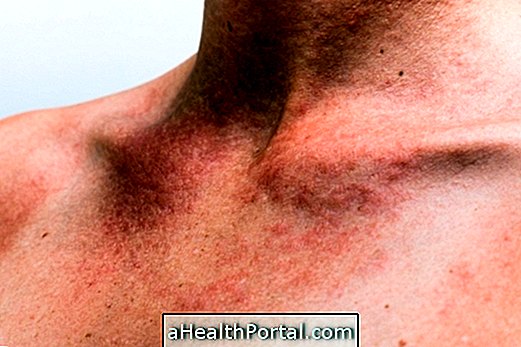
Polycythemia usually does not produce symptoms, especially if the increase in the number of red blood cells is not so great, being perceived only through the blood test. However, in some cases, the person may experience constant headache, blurred vision, red skin, excessive tiredness and itching of the skin, especially after bathing and may indicate polycythemia.
It is important for the person to have a blood count regularly and, if any polycythemia-related symptoms occur, go to the doctor immediately, because increasing the blood viscosity due to the increase in the number of red blood cells increases the risk of stroke, acute myocardial infarction myocardium and pulmonary embolism, for example.
How is the diagnosis made?
The diagnosis of polycythemia is made from the results of the hemogram, in which not only the increase in the number of red blood cells, but also the hematocrit and hemoglobin values are increased. See the blood count reference values.
According to the analysis of the blood count and the result of other tests performed by the person, polycythemia can be classified in:
- Primary polycythemia, also called polycythemia vera, is a genetic disease characterized by the abnormal production of blood cells. Understand more about polycythemia vera;
- Relative polycythemia, which is characterized by the increase in the number of red blood cells due to the decrease in plasma volume, as in the case of dehydration, for example, not necessarily indicative of a higher production of red blood cells;
- Secondary polycythemia, which occurs due to diseases that can lead to increase not only the number of erythrocytes, but also other laboratory parameters.
It is important that the cause of polycythemia is identified so that the best type of treatment is established, avoiding the appearance of other symptoms or complications.
Main causes of polycythemia
In the case of primary polycythemia, or polycythemia vera, the cause of increased production of red blood cells is a genetic disorder that causes deregulation in the production process of red blood cells, leading to increased red blood cells and sometimes leukocytes and platelets .
In relative polycythemia, the main cause is dehydration, because in these cases there is loss of body fluids, leading to an apparent increase in the number of red blood cells. Usually in the case of relative polycythemia levels of erythropoietin, which is the hormone responsible for regulating the process of producing red blood cells, are normal.
Secondary polycythemia can be caused by a number of conditions that can lead to an increase in the number of red blood cells, such as cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, obesity, smoking, Cushing's syndrome, liver diseases, early myeloid leukemia, lymphoma, renal disorders and tuberculosis. In addition, the number of red blood cells may increase due to prolonged use of corticosteroids, vitamin B12 supplements and medicines used in the treatment of breast cancer, for example.
How to treat
The treatment of polycythemia should be guided by a hematologist in the case of the adult or by a pediatrician in the case of the baby and the child, and depends on the cause of the increase in the number of red blood cells.
Usually the treatment aims to decrease the amount of red blood cells, make the blood more fluid and thus relieve the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. In the case of polycythemia vera, for example, therapeutic phlebotomy, or bleeding, may be recommended, where excess red blood cells are withdrawn.
In addition, your doctor may recommend the use of medications, such as aspirin, to make your blood more fluid and reduce the risk of clotting, or other medicines, such as Hydroxyurea or Interferon alfa, for example to decrease blood pressure. amount of red blood cells.