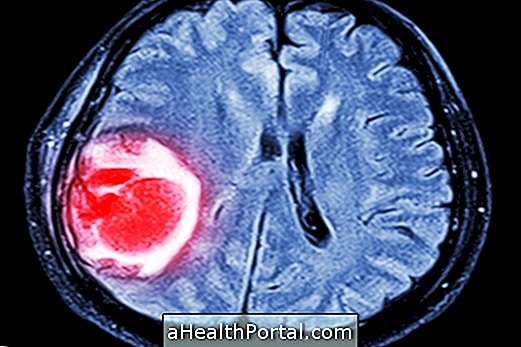
Glioblastoma multiforme is a type of brain cancer of the gliomas group, because it affects a specific group of cells called "glial cells", which help in the composition of the brain and in the functions of the neurons.
This is a type of aggressive tumor, classified as grade IV, because it has a great ability to infiltrate and grow along the brain tissue, and can cause symptoms such as headache, vomiting or seizures, for example.
The treatment consists of total withdrawal of the tumor concomitantly with radiotherapy and chemotherapy, however, due to its aggressiveness and fast growth, it is hardly possible to cure this cancer, which has a median survival of 14 months. is not a rule and is variable according to the severity, size and location of the tumor, in addition to the clinical conditions of the patient.
It should be remembered that medicine has increasingly advanced the search for treatments both to increase survival and to improve the quality of life of people with this cancer.
Main symptoms
Although rare, glioblastoma multiforme is the most common cause of malignant brain tumors with cerebral origin, and is more common in people over 45 years of age. Symptoms range from mild to severe depending on their location in the brain and size, and some of the most common include:
- Headache;
- Changes in the motor, such as loss of strength or change in walking;
- Visual changes;
- Speech disorders;
- Cognitive difficulties, such as reasoning or attention;
- Personality changes, such as apathy or social avoidance;
- Vomiting;
- Seizures.
As the disease reaches more advanced or terminal phases, the symptoms may intensify and compromise the ability to accomplish daily activities and care.
In the presence of symptoms that indicate this cancer, the doctor may request brain imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging, that will visualize the tumor, however, confirmation is only made after biopsy and analysis of a small piece of tumor tissue.
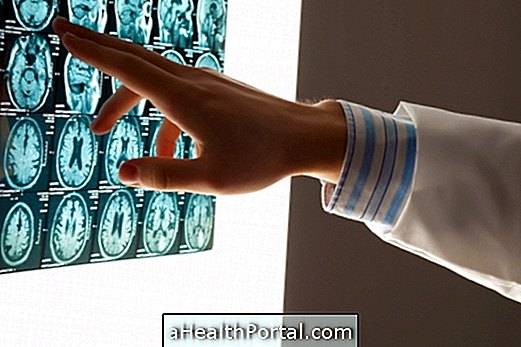
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of glioblastoma multiforme should be done as soon as possible after diagnosis, with oncologist and neurologist follow-up, and it is done with:
- Surgery : consists of the removal of all visible tumor in the image examination, avoiding to leave compromised tissues, being the first stage of the treatment;
- Radiation therapy : which is done with radiation emission as an attempt to eliminate the remaining tumor cells in the brain;
- Chemotherapy : done in conjunction with radiotherapy, improving its effectiveness. The most commonly used chemotherapeutic agent is Temozolomide, which is able to delay the progression of the disease. Check out what are and how to deal with the side effects of chemotherapy.
In addition, the use of medicines such as corticosteroids or anticonvulsants can be used to relieve some symptoms of the disease.
As it is a very aggressive tumor, the treatment is complex, and most of the time there is relapse, which makes the chances of cure difficult. Thus, decisions about treatment should be individualized for each case, taking into account the clinical picture or the existence of previous treatments, and should always prioritize the patient's quality of life.
It is also important to remember that we have sought to develop new drugs to improve the efficacy of glioblastoma treatment, such as gene therapy, immunotherapy and molecular therapies, in order to better target the tumor and facilitate recovery.






.jpg)