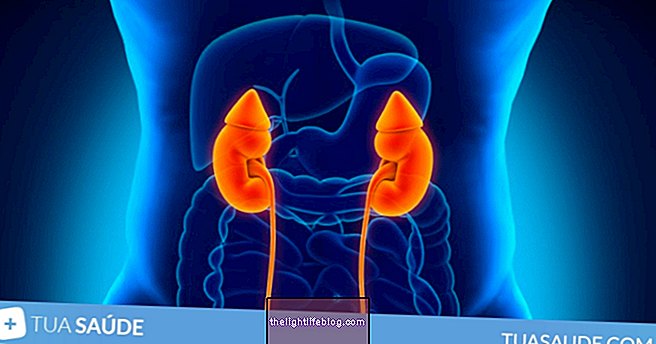
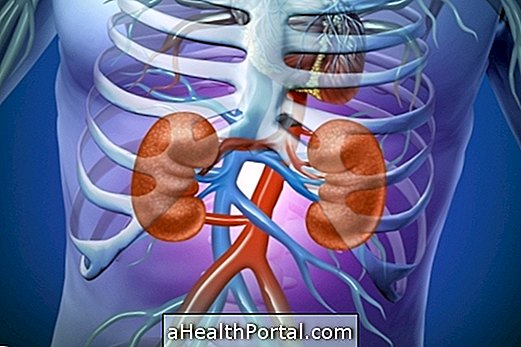
Kidney failure is the inability of the kidneys to filter the blood by eliminating bad substances such as urea or creatinine, for example, that can build up in the body when the kidneys are not working well.
Renal failure may be acute or chronic, and acute renal failure is characterized by a rapid reduction of renal function, whereas chronic renal failure may be due to factors such as dehydration, urinary tract infection, hypertension, or urinary obstruction. example.
Generally, acute renal failure is curable, but chronic renal failure is not always curable, and treatment is usually done by hemodialysis or kidney transplantation to improve the patient's quality of life and promote well-being. See how it is done and with is the kidney transplant recovery.
Symptoms of kidney failure
Renal failure may manifest itself through various symptoms, depending on whether acute or chronic, such as:
Signs of acute renal failure:
- Little urine, dark yellow and strongly smelling;
- Easy fatigue and shortness of breath;
- Pain in the lower back;
- Swelling of the legs and feet;
- Easy fatigue with shortness of breath;
- High pressure;
- Fever greater than 39ºC;
- Coughing up blood;
- Lack of appetite and presence of nausea and vomiting;
- Small lumps on the skin.
In addition, changes in blood and urine tests may occur, and the presence of proteins in the urine may be identified, as well as altered amounts of urea, creatinine, sodium, and potassium in the blood. Learn how to identify kidney malfunction.
Signs of chronic renal failure:
- The urge to urinate frequently, especially at night, waking up to urinate;
- Urine with strong odor and foam;
- Very high blood pressure that can result in stroke or heart failure;
- Sensation of very high body weight;
- Tremors, especially in the hands;
- Severe tiredness;
- Weak muscles;
- Frequent cramps;
- Tingling in the hands and feet;
- Loss of sensation;
- Convulsions;
- Yellowish skin;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Development of a small white layer on the skin, similar to dust, because urea crystallizes in sweat.
When observing these symptoms it is advised to consult with a nephrologist doctor so that examinations can be requested to diagnose the renal insufficiency and, thus, to indicate the appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis can be made based on symptoms and on tests such as ultrasound, MRI, CT scan, as well as urine and blood tests such as potassium, urea and creatinine. See how the blood creatinine dosage and reference values are made.

Main causes
Acute and chronic renal failure can occur due to:
- Reduced amount of blood in the kidney due to dehydration, poor kidney function or low blood pressure;
- Injury of the kidneys due to kidney stones or toxic substances like medicines;
- Interruption of urine passage, caused by enlarged prostate or presence of tumor.
- Sepsis, in which bacteria can reach the kidney and other parts of the body, causing damage to the organ;
- Polycystic kidney disease, which is characterized by the presence of various cysts in the kidney, which may impair its functioning;
- Use of excess drugs and protein supplements, as they may cause damage to the organ or interfere with one of its functions;
- Hemolytic-uremic syndrome, a disease caused by a toxin produced by some bacteria and resulting in damage to blood vessels, hemolytic anemia and progressive loss of renal function
People who are more likely to develop kidney failure are those who are diabetic or hypertensive and who do not follow the proper treatment indicated by the doctor. In addition, a family history of kidney problems or people who have undergone a transplant before or are over 60 years of age are also more likely to develop this disease. See other causes of kidney failure.
How is the treatment done?
Treatment for renal failure should be guided by the nephrologist and the nutritionist, and may be done at home or in the hospital, depending on the severity of the disease. Learning to live with a chronic illness such as kidney failure is a delicate and time-consuming process that requires a lot of dedication and effort.
Most of the time, the treatment is done with the use of medicines like antihypertensives and diuretics, like Furosemide, for example. In addition, a diet high in carbohydrates and low in protein, salt and potassium, which should be indicated by a nutritionist. Learn more about treating kidney failure.
In more severe cases, such as chronic renal failure, it may be necessary to perform a kidney transplant or hemodialysis, which is a procedure that aims to filter the blood, removing all impurities that the kidneys can not filter. See how hemodialysis is done.
Learn some tricks to feed yourself by properly watching: