Systemic sclerosis or scleroderma is a chronic disease in the connective tissue, which is characterized by hardening of the skin, joints, internal organs such as lungs, heart, kidneys, and also the wall of blood vessels.
Systemic sclerosis has no known cause, but it is known to be more common in women between the ages of 30 and 50, and manifests itself differently in carriers. Its evolution is also unpredictable, it can evolve quickly and lead to death, or slowly, causing problems in the skin without ever manifesting in the internal organs.
Patients with this disease feel as the main symptoms:
- swelling and numbness in the fingers and toes;
- difficulty in breathing and swallowing food;
- pains in the joints.
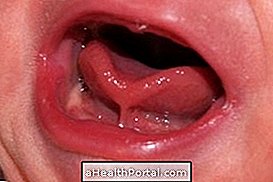
As the disease progresses, the skin creates a tense, stiff and dark aspect, preventing patients from changing their facial expressions, the veins of the body becoming more visible and coarse, becoming visible on the hands, mouth and tongue. In some cases, calcium tumors develop and wounds on the fingers and joints.
There is no cure for scleroderma and the treatment only softens the symptoms of the disease using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and penilcilamine.