Poisoning can occur when a person ingests, inhales, or comes in contact with a toxic substance such as cleaning products, carbon monoxide, arsenic, or cyanide, for example, causing symptoms such as uncontrollable vomiting, difficulty breathing, and confusion.
In these cases, it is important that:
- Call the Antivenus Information Center immediately on 0800 284 4343 or call an ambulance by calling 192;
- Decrease exposure to the toxic agent :
- Ingestion: gastric lavage is best performed at the hospital; however, while waiting for medical help, one can drink 100 g of powdered activated charcoal diluted in a glass of water for adults, or 25 g of this charcoal. children. Charcoal sticks to the toxic substance and prevents it from being absorbed in the stomach. It can be bought in pharmacies and some natural products stores;
- Inhalation: try to remove the victim from the contaminated environment;
- Skin contact: wash victim's skin with soap and water and remove clothing stained by substance;
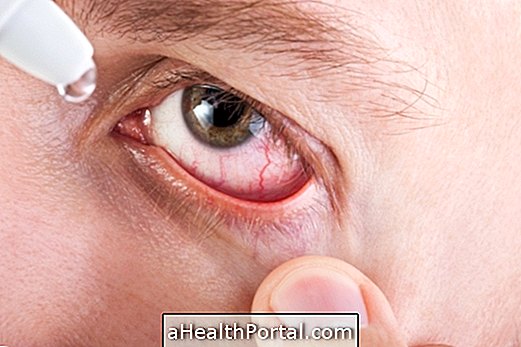
- Eye contact: Flush eyes with cold water for 20 minutes.
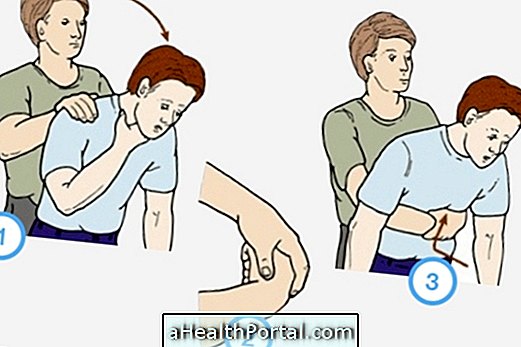
- Put the person on a lateral safety position, especially if he is unconscious to avoid suffocation should he vomit. Here's how to put someone in this position;
- Look for information on the substance that caused the poisoning by reading the label on the packaging of the toxic substance;
While awaiting the arrival of medical help it is important to be aware if the victim continues breathing, starting cardiac massage if they stop breathing. In cases of poisoning due to ingestion, if the victim has burns on the lips, they should be gently wetted with water, without allowing the victim to swallow, because the ingestion of water may favor the absorption of the poison.
See in this video how to handle in case of poisoning by ingestion:

Symptoms that may indicate poisoning
Some of the symptoms that may indicate that someone is poisoned and in need of medical help are:
- Burns and intense redness on the lips;
- Breath-smelling chemicals such as gasoline;
- Dizziness or mental confusion;
- Persistent vomiting;
- Difficulty breathing.
In addition, other signs, such as empty tablet packs, broken tablets, or intense odors from the victim's body, may be a sign that he or she was using some toxic substance and should call a physician immediately.
What not to do in case of poisoning
In case of poisoning, do not:
- Give liquid to the victim, as it may favor the absorption of some poisons;
- Causes vomiting if the victim has ingested a corrosive agent or solvent, unless otherwise directed by a healthcare professional.
Information collected from the victim, or local, should be provided to health care professionals as soon as they arrive on site.
If poisoning occurs from ingesting detergent, read what to do and how to avoid complications.