Gastric bypass, also known as Roux-en-Y bypass or Fobi-Capella surgery, is a type of bariatric surgery that can lead to the loss of up to 70% of the initial weight and consists of reducing the stomach and changing the bowel, leading the person to eat less, eventually losing weight.
As it is a type of surgery that causes a great alteration in the digestive system, the bypass is only indicated for people with BMI greater than 40 kg / m² or with a BMI greater than 35 kg / m² but who have already suffered some health problem derived of overweight and is usually only performed when other techniques, such as gastric band placement or gastric balloon, have not had the desired results.
Know the main types of bariatric surgery and when to use it.
What is the price of surgery?
The value of gastric bypass surgery depends on the clinic where it is performed and the necessary follow-up before and after surgery, varying between 15, 000 and 45, 000 reais, this already includes all the professionals involved in the pre, intra and postoperative, besides all the medicines.
In some cases, the bypass can be done at the SUS for free, especially when there is a risk of developing serious health problems due to overweight, and a rigorous evaluation by the gastroenterologist is necessary.
How Gastric Bypass Is Done
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is a complex surgery that is performed under general anesthesia and takes an average of 2 hours, and it is recommended to be admitted for 3 to 5 days. To do the bypass, the doctor needs to take several steps:
- Cut the stomach and intestine: a cut is made in the stomach next to the esophagus that divides it into two parts, a very small portion, in the form of a pouch, and a large portion that corresponds to the remaining stomach and which loses much of the its function by not storing food. In addition, a cut is made in the first part of the intestine, called jejunum;
- Attach a portion of the intestine to the smaller stomach: a direct passage is created for food in the form of a tube;
- Unite the part of the intestine that was attached to the large part of the stomach to the tube: this connection allows the food, which comes from the previous connection created, to mix with the digestive enzymes, occurring digestion.
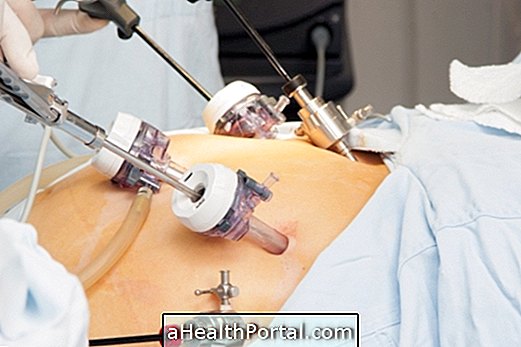
Usually, this surgery is done by a neovolaparoscopy, making 4 to 6 holes in the abdomen that allow the passage of a microchamber and the instruments to perform the surgery. According to this technique the surgeon observes the interior of the organism by a screen, commanding the instruments. Learn more at: Videolaparoscopy.
Surgery can also be performed by laparotomy, with the total opening of the abdomen occurring, but it is a procedure that presents more risks than laparoscopy.
The gastric bypass for weight loss causes a loss of up to 70% of the initial weight and allows to maintain this loss over the years, because in addition to the patient is quickly sated, the alteration of the intestine, leads to a less absorption of what is ingested.
How is recovery
Recovery from gastric bypass is slow and can take anywhere from 6 months to 1 year, with the most intense weight loss in the first 3 months. To ensure a better recovery, it is necessary to have some care such as:
- Follow the diet indicated by the nutritionist, which is changing over the weeks. Learn more at: Food after Bariatric Surgery.
- Take vitamin supplements, such as iron or vitamin B12 because of the risk of chronic anemia;
- Do the dressing of the abdomen at the health clinic one week after the surgery;
- Remove the drain, which is a container where fluids in excess of the stoma drain, depending on the medical indication.
- Take antiemetic like Omeprazole before meals to protect the stomach as directed by a doctor;
- Avoid efforts in the first 30 days to prevent any staples from loosening.
The results of this bariatric surgery come in over the weeks, however, it may be necessary to undergo cosmetic surgery, such as abdominoplasty, 1 to 2 years later to remove excess skin. Here's how this surgery is done in: Tummy Tuck.
Learn more about recovery in: How Bariatric Surgery Recovery Is.
Possible Complications
It is common for the person who does a bypass to feel nausea, vomiting, heartburn or diarrhea during the first month after surgery. However, the most serious complications of this surgery include:
- Fistula of scars from the stomach or intestines, which can increase the chances of infections, such as peritonitis or sepsis, for example;
- Severe bleeding in the scar area of the stomach;
- Chronic anemia, mainly due to vitamin B12 deficiency;
- Dumping syndrome, which causes symptoms such as nausea, intestinal cramps, fainting and diarrhea after a person has eaten. See more in: How to Relieve the Symptoms of Dumping Syndrome.
In some cases, the person may even need another surgery to correct the problem.