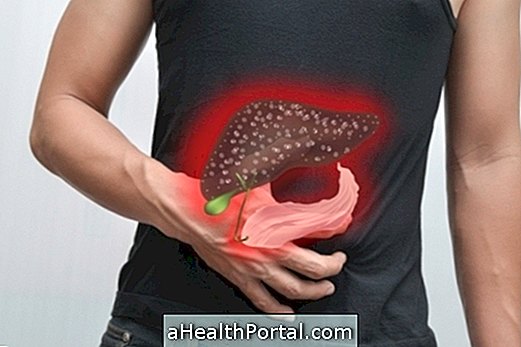
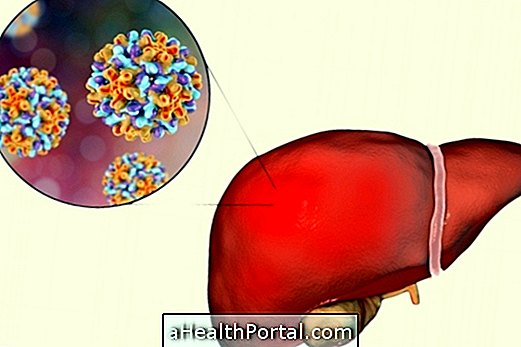
Chronic hepatitis is an inflammation in the liver that has no cure for at least 6 months. This type of hepatitis can last for decades, developing slowly, and can cause cirrhosis or liver failure.
About 80% of types of hepatitis can progress to chronic hepatitis, but hepatitis A and E are exceptions, as they usually heal in a relatively short time.
Symptoms of Chronic Hepatitis
They are symptoms of chronic hepatitis:
- Fatigue
- Joint pain;
- Redness on the skin;
- Memory loss;
- Lack of appetite;
- Fever;
- Malaise.
Causes of Chronic Hepatitis
The causes of chronic hepatitis can be:
- Presence of a hepatitis virus in the blood;
- Inadequate intake of medications,
- By autoimmune diseases,
- Alcohol or drug abuse or
- Genetic predisposition.
Diagnosis of Chronic Hepatitis
The diagnosis of chronic hepatitis is based on the symptoms presented by the patient and a histopathological examination of a fragment of the liver obtained through a biopsy.
Through the biopsy the severity of the inflammation will be detected and the doctor will know if there has been development for cirrhosis or fibrosis.
Treatment for Chronic Hepatitis
Treatment for chronic hepatitis depends on the severity of liver damage and its causes. Usually, steroids are used indefinitely. When the cause of chronic hepatitis is an autoimmune disease, treatment should be done accurately, as this cause can lead to the development of cirrhosis and liver failure.
A drug called interferon alpha may also be used.
Is Chronic Hepatitis Contagious?
Chronic hepatitis caused by viruses is contagious and can be transmitted through contact with blood contaminated with the hepatitis virus. Hepatitis A and hepatitis E, although contagious, do not become chronic in most people. However, drug-induced hepatitis and autoimmune hepatitis are not contagious.
Chronic hepatitis has a cure
Chronic hepatitis is cured if treatment is properly and accurately done and liver transplantation is not always necessary.
Useful links:
- Hepatitis
- Autoimmune hepatitis