Symptoms of a stroke (stroke), also known as a stroke or stroke, can arise from time to time, and depending on the part of the brain that is affected manifests differently.
However, there are some symptoms that can help identify this problem quickly, such as:
- Severe headache that comes on suddenly;
- Decreased strength on one side of the body, which is visible on the arm or leg;
- Loss of sensitivity of a part of the body, not identifying the cold or heat, for example;
- Difficulty standing or sitting, because the body falls to one side, unable to walk or dragging one of the legs;
- Vision changes, such as partial loss of vision or blurred vision;
- Asymmetrical face with crooked mouth and drooping eyebrow;
- Difficulty lifting an arm or holding objects, as the arm is dropped;
- He is speechless, slow, or very low and often imperceptible;
- Uncommon and uncontrolled movements, such as tremors;
- Drowsiness or even loss of consciousness;
- Loss of memory and mental confusion, not being able to perform simple orders, such as open your eyes and, being able to be aggressive and not know to refer to the date or its name, for example;
-
Nausea and vomiting .
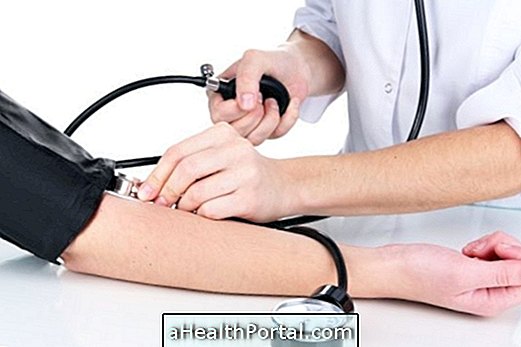
Despite this, stroke can also happen without generating any visible symptoms, being discovered in tests that are performed for any other reason. People who are more likely to have a stroke are those who have high blood pressure, are overweight, or have diabetes, so they should see their doctor regularly to avoid complications.
What to do in case of suspicion
If a stroke is suspected, a SAMU test should be done, which consists of:

Generally, people who are suffering from a stroke are not able to perform the actions requested in this test. So if this happens, the victim must be laid aside in a safe place and call the SAMU by calling 192, always being aware if the victim continues to breathe normally and if he stops breathing he must start the cardiac massage .
What can be the sequelae of stroke
After a stroke, the individual may have sequelae, which may be temporary or very severe and, due to lack of strength, can prevent him from walking, dressing or eating alone, for example.
In addition, other consequences of stroke include difficulty communicating or understanding orders, frequent choking, incontinence, loss of vision or even confusing behaviors and aggressiveness, which makes it difficult to relate to family and friends.
It is very important to know that there are treatments that help to decrease the sequelae of stroke. Physical therapy sessions can help you regain your movements. Speech therapy sessions help to recover speech and improve communication. And occupational therapy sessions help to improve the quality of life and well-being of the individual.
To avoid these sequels the most important is to prevent the stroke from happening. So learn what you can do to reduce your risk of having a stroke.








-e-como-tratar.jpg)