Hand-foot-mouth syndrome is a highly contagious disease that occurs most often in children under 5 years of age, but can also occur in adults, and is caused by the coxsackie virus, which can be transmitted from person to person or through contaminated food or objects.
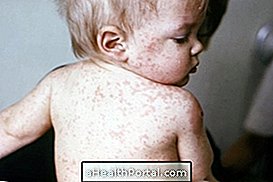
Symptoms of hand-foot-mouth syndrome usually only appear after 3 to 7 days of infection with the virus and include fever higher than 38 ° C, sore throat and poor appetite. After 2 days of the onset of the first symptoms, there are painful sores in the mouth and painful blisters on the hands, feet and sometimes in the intima which may scratch.
Treatment of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome should be guided by the pediatrician or general practitioner and may be done with fever remedies, anti-inflammatories, itch remedies, and thrush ointments to relieve symptoms.
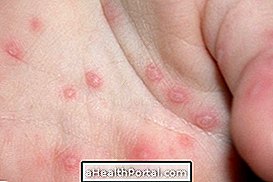

Main symptoms
Symptoms of hand-foot-mouth syndrome usually appear after 3 to 7 days after virus infection and include:
- Fever above 38ºC;
- Sore throat;
- Difficulty swallowing;
- Much salivation;
- Vomiting;
- Malaise;
- Diarrhea;
- Lack of appetite;
- Headache;
- Appearance of red spots or blisters on the hands and feet and mouth ulcers 2 to 3 days after the onset of fever.
The diagnosis of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome is made by the pediatrician or general practitioner through the analysis of symptoms and blemishes.
Because of some symptoms, this syndrome can be confused with some diseases, such as herpangina, which is a viral disease in which the baby has herpes-like mouth sores, and scarlet fever, in which the child has scattered red spots by the skin. Therefore, the doctor may request additional laboratory tests to close the diagnosis. Understand more about herpangina and know what is scarlet fever and its main symptoms.
How transmission occurs
The transmission of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome occurs through coughing, sneezing and saliva and direct contact with blisters that have burst or infected feces, especially during the first 7 days of the disease, but even after recovery, the virus can still be passed through the stool for about 4 weeks.
In addition, the virus can be transmitted through contaminated objects or food. Therefore, it is important to wash the food before consumption, change the baby's diaper with a glove and then wash your hands and wash your hands thoroughly after using the toilet. See when and how to wash your hands properly.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment of the hand-foot-mouth syndrome should be pediatrician or general practitioner-oriented and may be ugly with fever remedies, such as Paracetamol, anti-inflammatories such as ibuprofen, itch remedies such as antihistamines, for canker sores, or lidocaine, for example.
The treatment lasts about 7 days and it is important that the child does not go to school or daycare during this time to avoid contaminating other children. Learn more about treating hand-foot-mouth syndrome.