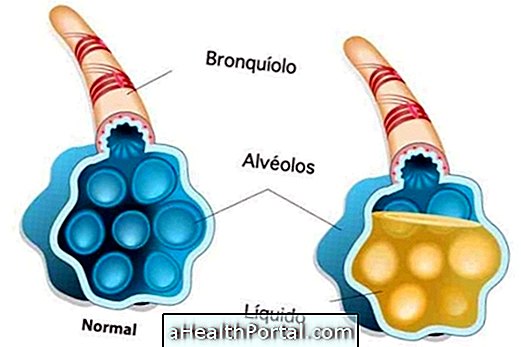
Pneumonia is a respiratory disease caused by viruses, bacteria or fungi. Fever above 37.8 ° C, shortness of breath, shortness of breath and chills are some of the earliest symptoms of pneumonia, a contagious disease that causes inflammation of the lung and accumulation of fluid within the lung alveoli. When the infection affects different regions of the lung, it is called Bronchopneumonia.
Symptoms of pneumonia may come on suddenly or gradually, appearing when the immune system is weakened, as it is after a cold or flu that does not go away or worsens over time. Pneumonia can be caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites, but the most common are bacterial pneumonia that are treated with antibiotics. Here's how to identify if it's bacterial pneumonia.
What are the main symptoms
Although there are different types of pneumonia, in most cases the symptoms are similar, varying only the treatment indicated by the pulmonologist. To know if you may have pneumonia, select your symptoms:
- 1. Fever above 37.5 ° C Yes No
- 2. Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath Yes No
- 3. Breathing faster than normal Yes No
- 4. Dry cough Yes No
- 5. Cough with greenish or bloody phlegm Yes No
- 6. Chest pain Yes No
- 7. Constant headache Yes No
- 8. Frequent tiredness or muscle pain Yes No
- 9. Intense night sweats Yes No

These symptoms can also vary slightly depending on whether it is an adult, baby or elderly person. Therefore, in addition to the indicated symptoms, a baby or a child, who have more difficulty explaining what they feel, may also have other signs such as agitation, tremors, vomiting, decreased appetite and, in babies, excessive crying.
In the elderly, other symptoms such as confusion and memory loss may be associated with fever, difficulty breathing, and coughing.
As the doctor confirms that it is pneumonia
The diagnosis of pneumonia is usually made through the evaluation of symptoms and an X-ray examination to check the health status of the lungs. In addition, other tests such as a conventional blood test, a catarrh examination, or an arterial blood test may also be ordered to check for changes in blood and to identify the type of infection present.
Treatment Options
Treatment for pneumonia can be done with antibiotics, but keeping the airways clear and eating easily digestible foods that boost immunity are excellent ways to recover faster. Thus, the treatment indicated by the pulmonologist can be done with the following options:
1. Medicines to eliminate the virus or bacteria
In most cases, treatment of pneumonia can be done at home by taking antibiotics such as amoxicillin, clavulanic acid or azithromycin, which fight the microorganisms responsible for causing the disease. After confirming the pneumonia, in most cases it is not possible to immediately discover which microorganism causes the disease. However, because bacteria are primarily responsible, the doctor may choose to prescribe antibiotics, which should be changed later if symptoms persist or worsen.
In children less than 1 year of age, and in the elderly over 70 years and who has other health problems associated with diabetes, the doctor may prefer that the person be hospitalized to receive treatment in the hospital. In more severe cases, when practically the person can not breathe alone, it may be necessary to stay in the ICU.
2. Home treatment
The treatment can last up to 21 days and some care is recommended, which can be seen as a home treatment for pneumonia, such as:
- Drink a lot of water;
- Cover your mouth to cough and wash your hands regularly to avoid transmission of the disease;
- Avoid going to public or closed places;
- Make nebulisations with saline;
- Rest and rest, avoiding making efforts;
- Do not take cough medicine;
- Avoid sudden changes in temperature.
These precautions prevent the transmission and worsening of the disease, ensuring correct recovery.
3. What to eat to recover faster
Food is also a very important factor throughout the recovery process, and it is recommended to bet on the consumption of vegetable soups, echinacea tea, garlic, onion or propolis extract. Watch our nutritionist's video for other tips:

What are the causes of pneumonia?
Some conditions that can cause pneumonia include:
- When the person has the flu and the virus or bacteria present in the nose or throat reaches the lung;
- When a person inhales an object into the lungs, as can happen when the child puts a beanstalk or a small toy in the nose and it stops in the lung;
- When the person vomits and aspirates the contents that were present in the stomach, causing inflammation of the lung tissues;
- When the person uses some equipment to help breathe, like CPAP, and it is dirty, with viruses or bacteria going directly to the lung;
- When the person was hospitalized for up to 48 hours before the symptoms appeared, which indicates that the virus or bacteria reached the person's lungs when the patient was still in the hospital, but the symptoms only began to manifest days later.
The most affected people are children under 5 years of age and the elderly over 70, who have a healthier fragile, getting sick more easily. However, anyone can get pneumonia, especially if they have any changes such as difficulty swallowing, failure to eliminate phlegm or weakened immune systems because they are being treated for cancer or HIV, for example.