Conductive hearing loss also known as hearing loss is due to a problem in the middle ear or outside of the ear, which prevents the sound from reaching the inner ear clearly and perceptibly. Usually, this problem occurs because the ear canal becomes clogged or the ear bones, such as the stirrup, become more rigid, which prevents the eardrum from moving, for example in the case of otosclerosis.
Hearing impairment may be unilateral or affect both ears, and conductive hearing loss is generally mild to moderate, ranging from 25 to 65 decibel, and therefore the individual can hear the sounds even if he can not perceive everything was clear.
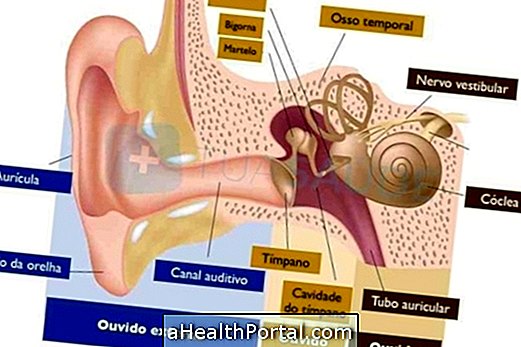
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss
The most common cause of conductive hearing loss is obstruction of the ear canal, caused by the excessive presence of wax. However, it may occur due to:
- Infection in the ear canal or middle ear;
- Tired eardrum;
- Fluid in the middle ear, such as water;
- Presence of foreign objects in the ear canal;
- Otosclerosis, which is a malfunction of the ossicles of the ear;
- Tumors.
Normally, the hearing loss is temporary, however, it is necessary to go to the otolaryngologist to detect the cause and start the most appropriate treatment. To know the most common causes of hearing loss read: Find out what are the main causes of hearing loss.
Symptoms of conductive hearing loss
Decreasing hearing in the case of conductive hearing loss causes symptoms such as:
- Listen to the low or muffled sounds;
- Ear pain;
- Swelling of the ear;
- Capped ear sensation;
- Ringing in the ear;
- Dizziness;
- I get sick.
To treat conductive hearing loss, it is necessary to know what caused the hearing loss, and in some cases it is necessary to use a hearing aid or have a surgery to place with an implant in the middle ear and thus to hear better. To learn how to treat hearing loss read: Know the treatments for hearing loss.