Some of the determining factors for the appearance of mouth cancer are excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages and cigarettes, sun exposure, HPV in the mouth, poor hygiene of the mouth or use of maladaptive dentures.
Mouth cancer is a type of tumor, diagnosed by the dentist, that can appear on the tongue, the roof of the mouth, gums, cheeks, lips or the garment, producing symptoms such as wounds that do not heal, difficulty chewing or staining red, for example.
This is one of the most common types of cancer in the world, and often affects men over 45 years of age and can be fatal when left untreated.
What can cause mouth cancer
Mouth cancer can be caused by some common situations like cigarettes, which include the use of cahimbo, cigar or even the act of chewing tobacco, because the smoke contains carcinogenic substances, such as tar, benzopyrenos and aromatic amines. Moreover, the increase in temperature in the mouth facilitates an aggression of the oral mucosa, which makes it even more exposed to these substances.
The excess of alcoholic beverages is also related to oral cancer although it is not known exactly which mechanism causes, it is known that the alcohol facilitates the entrance of the ethanol residues, like the aldehydes, by the mucosa of the mouth favoring the cellular alterations.
Sun exposure on the lips without proper protection, such as lipsticks or sunscreen-based balms, is also one of the factors that influence the development of lip cancer, which is very common in Brazil, and especially affects people with fair skin, working exposed to the sun.
In addition, food also favors the establishment of this type of cancer, with foods that cause inflammation of animal foods such as meat and fat, while vegetables and fruits help the body to defend itself against this disease.
Infection with the HPV virus in the mouth also seems to increase the risk of oral cancer, so to protect against this virus it is necessary to use the condom even during oral sex.
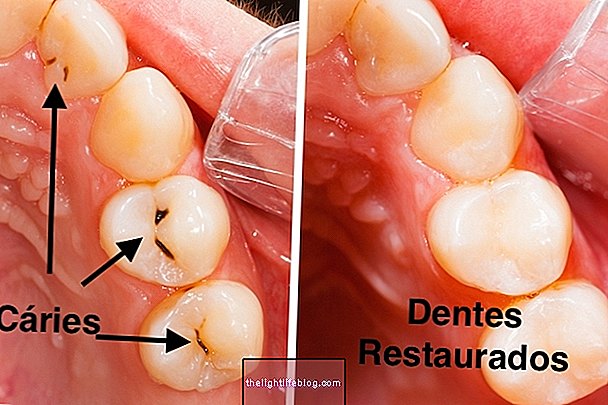
Poor oral hygiene and the use of maladaptive dentures are also factors that facilitate the development of oral cancer, but on a smaller scale.
How to identify
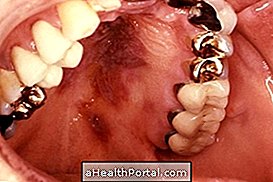

The best way to identify the cancer of the mouth is to be attentive to the health of the mouth, and to observe if there are changes in the lips, cheeks, tongue or sky of the mouth.
The cancer of the mouth does not always hurt especially in the initial phase, beginning to hurt at a later stage. The symptoms that the person may notice may take months to appear, but the dentist may suspect a major change, so it is important to go to the dentist at least once a year.
Early symptoms of oral cancer include:
- Wound in the mouth that takes more than 2 weeks to heal;
- Presence of a lump in the mouth, which may not cause pain;
- White or red spots on the tongue, cheeks, sky of the mouth or under the tongue;
- Sore throat that does not get better.
In addition, other symptoms that may appear over time are constant pain in the mouth, feeling that the teeth are loose and loss of teeth for no apparent reason. Learn more details of Mouth Cancer Symptoms.
What to do
In case of suspicion or in the presence of any of these symptoms you should consult a dentist for an oral examination or, if necessary, take a biopsy to miss the diagnosis of cancer and start the appropriate treatment because it may be only a benign lesion.
The treatment for mouth cancer should be done by a dentist or an oncologist and is usually started with surgery to remove the cancer cells from the mouth, throat or lips. However, because of the location of the tumor or the severity of the case, it may not be possible to remove all of the cancer cells, so it may be necessary to use radiation therapy or chemotherapy to eliminate the remaining cells.
Usually when mouth cancer is diagnosed at an early stage, the chances of cure are great. See more details of Treatment for cancer of the mouth.
How To Prevent Mouth Cancer
To prevent mouth cancer it is recommended to avoid all risk factors, and have good oral hygiene habits. To do this you must:
- Brush your teeth at least 2 times a day with a toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste;
- Eat healthy foods such as fruits, vegetables and cereals, avoiding eating meat and processed foods daily;
- Use condoms in all sexual relations, even in oral sex, to avoid contamination with HPV;
- Do not smoke and do not get too exposed to cigarette smoke;
- Moderately drink alcoholic beverages;
- Use lipstick or lip balm with sun protection factor, especially if working exposed to the sun.
In addition, it is recommended to treat any changes in the teeth early, and to follow all dentist guidelines, and it is important not to use another person's dental prosthesis or mobile orthodontic appliance because they may cause areas of greater pressure that compromise the oral mucosa, facilitating the entry of harmful substances.