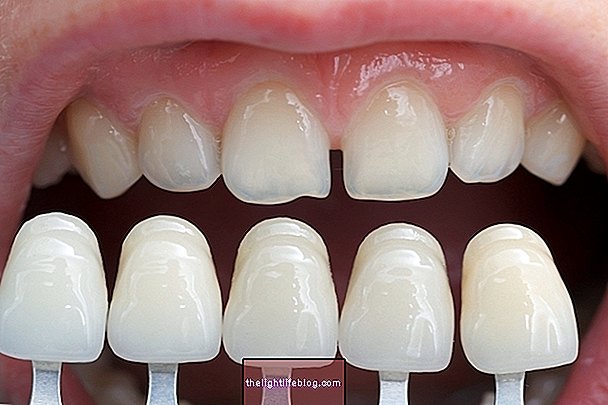
Periodontitis is a bacterial infection that generates inflammation in the gums, causing bleeding when brushing teeth, while eating or while brushing teeth. In addition, the teeth are slowly separating, becoming crooked and can easily fall because they are no longer properly adhered to the jaw bone. Its main cause is the permanence of a group of bacteria inside the mouth that are slowly destroying the structure of bones and gums.
This chronic inflammation may not be noticed when it arises, still in youth, but is permanent tends to worsen bone loss over the years, until around the age of 45, when one usually sees soft, crooked and separated teeth. In some cases it is only noticeable that there is a problem of oral health when the teeth are soft and begin to fall, without any apparent explanation.

How to Identify Periodontitis
Periodontitis can be localized, affecting only one or other tooth, or generalized, when it affects all teeth at the same time. The change in the appearance of the teeth is what most draws the attention of the person, or person close, but it is the dentist who makes the diagnosis of periodontitis, taking into account the signs presented.
Symptoms that may be present include:
- Bad breath;
- Very red gums;
- Swollen gums;
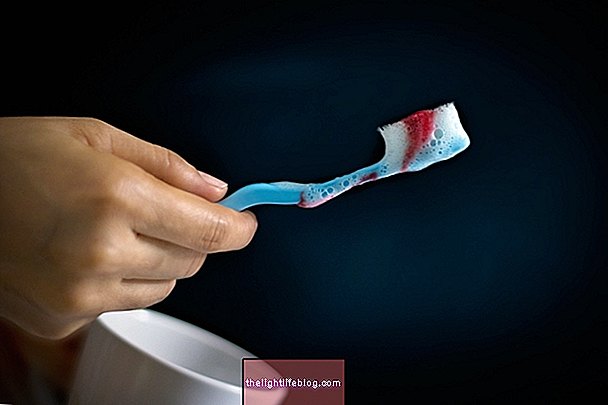
- Bleeding gums after brushing teeth or eating;
- Crooked teeth;
- Softening of teeth;
- Tooth loss;
- Increased space between teeth;
- Wake up with blood on the pillow.
The diagnosis of periodontitis can be made by the dentist when observing the region, but a panoramic X-ray examination may be helpful in assessing the severity of the disease. Cases in the parent's family with periodontitis as well as smoking increase the chances of the disease starting.
Treatment for Periodontitis
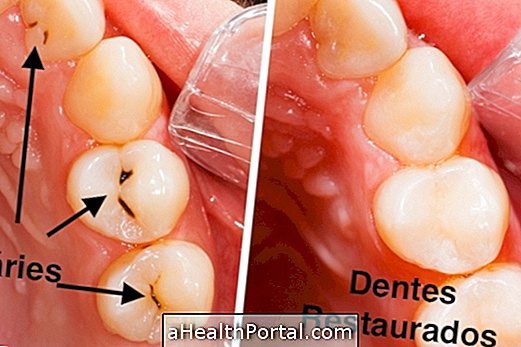
The treatment to end periodontitis involves scraping the root of the tooth in the office and under anesthesia to remove tartar plaque and bacteria that are destroying the bone structure that supports the tooth. The use of antibiotics may be part of the treatment.
Maintenance at the dentist periodically slows the progression of this inflammation and helps control the disease, decreasing bone loss and preventing tooth loss. Also, no smoking, brushing your teeth daily and flossing are ways to control and cure periodontitis.