Salivary glands are structures located in the mouth that have the function of producing and secreting saliva, which has enzymes responsible for facilitating the digestive process of food and for maintaining lubrication of the throat and mouth, preventing dryness.
In some situations, such as infections or the formation of salivary stones, the function of the salivary gland can be impaired, resulting in symptoms such as swelling of the affected gland, which can be perceived through the swelling of the face, as well as pain to open the mouth and to swallow , for example. In these situations, it is important that the person goes to the dentist or general practitioner so that the cause is investigated and appropriate treatment is started.

Function of salivary glands
The main function of the salivary glands is the production and secretion of saliva, which happens when there is food in the mouth or as a result of olfactory stimulation, in addition to happening regularly with the objective of maintaining lubrication and hygiene of the mouth, as it has enzymes capable of bacteria and thus reduce the risk of caries.
The saliva produced and secreted is also rich in digestive enzymes, such as ptialin, also known as salivary amylase, which is responsible for the first stage of the digestive process, which corresponds to starch degradation and softening of the food, allowing it to be swallowed. Understand how the digestive process works.
Salivary glands are present in the mouth and can be classified according to their location in:
- Parotid glands, which is the largest salivary gland and is located in front of the ear and behind the mandible;
- Submandibular glands, which is present in the posterior part of the mouth;
- Sublingual glands, which are small and are located under the tongue.
All salivary glands produce saliva, however the parotid glands, which are larger, are responsible for the greater production and secretion of saliva.
What problems can happen?
Some situations can interfere with the functioning of the salivary glands, which can have consequences for the person's well-being and quality of life. The main alteration related to the salivary gland is the obstruction of the salivary duct due to the presence of stones formed at the site.
The changes in the salivary glands can vary according to their cause, evolution and prognosis, the main changes being related to these glands:
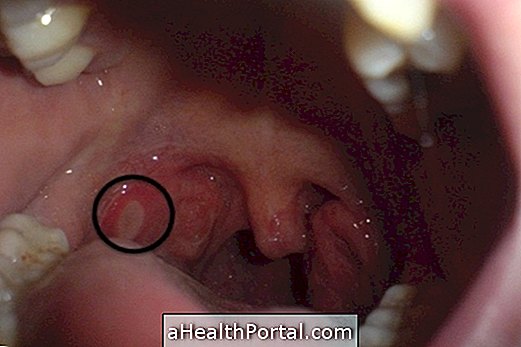
1. Sialoadenitis
Sialoadenitis corresponds to inflammation of the salivary gland due to infection by viruses or bacteria, obstruction of the duct or presence of salivary calculus, resulting in symptoms that may be uncomfortable for the person, such as constant pain in the mouth, redness of the mucous membranes, swelling of the region below dry tongue and mouth.
In the case of sialoadenitis involving the parotid gland, it is also possible that swelling is noticed on the side of the face, which is where this gland can be found. Know how to recognize the signs of sialoadenitis.
What to do: Sialoadenitis usually clears up on its own, so there is no need for any specific treatment. However, when it is persistent, it is recommended to go to the dentist or general practitioner to make the diagnosis and start treatment, which varies according to the cause, and antibiotics may be indicated in case of infection, or use of anti-inflammatory drugs with the aim of reducing signs and symptoms.
2. Sialolithiasis
Sialolithiasis can be popularly defined as the presence of salivary stones in the salivary duct, causing its obstruction, which can be perceived through signs and symptoms such as pain in the face and mouth, swelling, difficulty in swallowing and dry mouth.
The cause of the formation of salivary stones is not yet known, but it is known that the stones are the result of the crystallization of substances present in saliva and that it can be favored by an inadequate diet or the use of some medications that are capable of reducing the amount of produced saliva.
What to do: The treatment for sialolithiasis should be recommended by the doctor and may vary according to the size of the stone. In the case of small stones, it may be recommended that the person drink enough water to encourage the salivary duct stone to escape. On the other hand, when the stone is very large, the doctor may recommend performing a small surgical procedure to remove the stone. Understand how sialolithiasis is treated.
3. Cancer of the salivary glands
Cancer of the salivary glands is a rare disease that can be perceived from the appearance of some signs and symptoms, such as the appearance of a lump on the face, neck or mouth, pain and numbness in the face, difficulty opening the mouth and swallowing and weakness in face muscles.
Despite being a malignant disorder, this type of cancer is totally treatable and curable, however it is important that the diagnosis is made quickly and the treatment started soon after.
What to do: In the case of cancer of the salivary glands, it is important that treatment be started as soon as possible in order to avoid metastasis and worsening of the person's clinical condition. Thus, depending on the type of cancer and its extent, the doctor may recommend surgery, to remove as many tumor cells as possible, in addition to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which can be performed alone or together.
Learn more about cancer of the salivary glands.
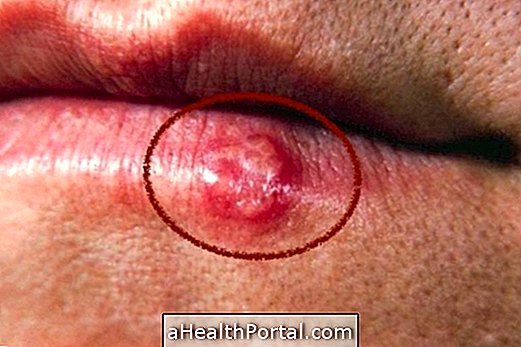
4. Infections
The salivary glands can also have their functioning altered and become swollen due to infections, which can be caused by fungi, viruses or bacteria. The most common infection is by the family virus Paramyxoviridae, which is responsible for mumps, also known as infectious mumps.
The signs of mumps appear up to 25 days after contact with viruses and the main symptom of mumps is swelling on the side of the face, in the region between the ear and chin, due to inflammation of the parotid gland, in addition to headache and face, pain when swallowing and when opening the mouth and feeling of dry mouth.
What to do: The treatment for mumps has the objective of relieving symptoms, and the use of pain relievers may be recommended by the doctor to relieve discomfort, as well as rest and ingestion of plenty of fluids, so that it is easier to eliminate the virus from the body. .
5. Autoimmune diseases
Some autoimmune diseases can also make salivary glands more swollen and impaired functionality, such as Sjögren's Syndrome, which is an autoimmune disease in which there is inflammation of various glands in the body, including salivary and lacrimal glands. As a result, symptoms such as dry mouth, dry eyes, difficulty swallowing, dry skin and an increased risk of infections in the mouth and eyes arise. Know other symptoms of Sjogren's Syndrome.
What to do: Treatment for Sjogren's Syndrome is done with the aim of relieving symptoms, so the doctor may recommend the use of lubricating eye drops, artificial saliva and anti-inflammatory drugs to decrease the inflammation of the glands.
Was this information helpful?
Yes No
Your opinion is important! Write here how we can improve our text:
Any questions? Click here to be answered.
Email in which you want to receive a reply:
Check the confirmation email we sent you.
Your name:
Reason for visit:
--- Choose your reason --- DiseaseLive betterHelp another personGain knowledge
Are you a health professional?
NoMedicalPharmaceuticalsNurseNutritionistBiomedicalPhysiotherapistBeauticianOther
Bibliography
- HALL, John. Treatise on medical physiology. 13 ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2017. 819-820.
- FLINT, Paul et al. Otorhinolaryngology: head and neck surgery. 6th ed. Rio de Janeiro: Elsevier, 2017. 589-603.