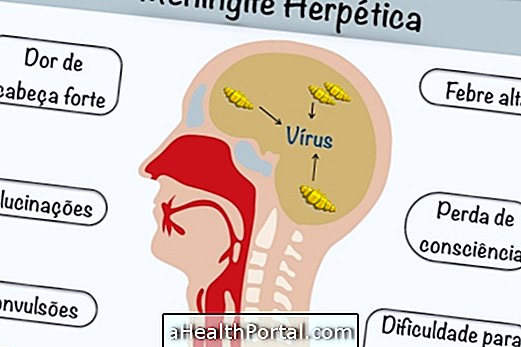
Herpetic meningitis is a type of inflammation of the membranes lining the brain and spinal cord caused by the herpes virus.
Despite being a viral meningitis, this type of meningitis is very serious and life-threatening, especially when it causes the so-called meningoencephalitis, which is an inflammation spread across several regions of the brain.
Thus, your treatment is usually done in the hospital and usually lasts 1 to 3 weeks, and can be even longer in babies.
Main symptoms
The main symptoms of herpetic meningitis are:
- High fever;
- Strong headache;
- Hallucinations;
- Mood and aggression changes;
- Convulsions;
- Difficulty in moving the neck;
- Loss of consciousness;
- Sensitivity to light.
In the presence of these symptoms, one should go to the medical emergency, especially after the onset of hallucinations, seizures and other neurological problems, since they indicate that parts of the brain were also affected by the virus.
How to confirm the diagnosis
The diagnosis is made initially from the evaluation of the symptoms of the disease, and then the doctor should ask for tests that confirm the meningitis, such as neurological exams, MRI, CT scan, electroencephalogram and blood tests.
In addition, the doctor may also order a lumbar puncture, in which a sample of the liquid from the cervical spine is withdrawn through a needle and taken for analysis to check for the presence of the virus. Learn more about how lumbar puncture is done.

How is the treatment done?
After confirmation of herpetic meningitis, treatment is done with the use of anti-viral drugs such as Aciclovir, which is normally given directly into the vein for 10 to 21 days, but in babies the duration of treatment may be longer.
In addition, medicines to reduce swelling in the brain and to prevent seizures should also be used and it is necessary to stay in the hospital.
See the other remedies that can be used to treat a viral meningitis.
Possible Complications
In general, if the appropriate treatment is started early, the patient shows signs of improvement after 2 days and recovers fully in about 1 month.
However, in some cases severe sequels may occur, such as difficulty moving and thinking properly, or vision, hearing or speech problems. In addition, when treatment is not done, this disease can lead to death.
Check out what kind of sequelae may appear after a case of meningitis.
How Transmission Happens
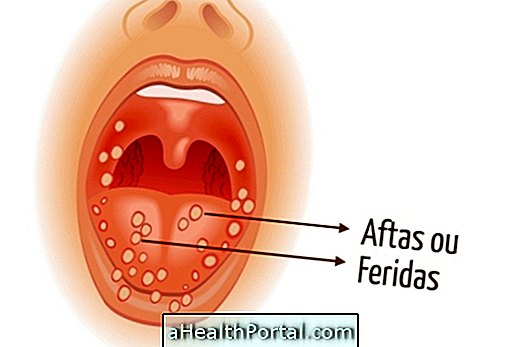
Herpetic meningitis affects individuals who have the herpes virus and who have weakened immune systems, as in AIDS cases, treatment for cancer and lupus, being transmitted by contact with the infected person in the same way as occurs with herpes.

Thus, to prevent herpes, one should avoid kissing people who have mouth sores caused by this virus and use condoms during intimate relationships. In addition, pregnant women who have genital herpes should prefer to undergo caesarean section to avoid transmission to the baby.
To better understand this disease, see what meningitis is and how to protect it.













.jpg)