The itching in the body arises when some reaction stimulates nerve endings of the skin, which can happen for several reasons, the main ones include some type of allergy or irritation in the skin, as by dryness, sweat or insect sting.
However, itching can not be related to diseases, which may be dermatological, infectious, metabolic or even psychological, such as dermatitis, mycosis, psoriasis, dengue, Zika, diabetes or anxiety, for example.
Depending on the cause, the itching by being alone or coming accompanied by other symptoms such as redness, lumps, spots, blisters or wounds, and these can be caused by an illness or formed by the frequent act of scratching. To treat it, it is important to discover and resolve its cause, but the symptom may be alleviated with an antiallergic or with a moisturizing or anti-inflammatory ointment prescribed by the general practitioner or dermatologist.
So some of the main causes of itching and what to do in each case include:
1. Allergic reactions
Any type of skin irritation can cause itching, and it is common for an allergy to happen. Some of the most common causes include:
- Excessive heat or sweat;
- Bug bite;
- Fabrics, cosmetics, such as soaps, creams and shampoos, or cleaning products;
- Animal hair or plants;
- Foods;
- Allergic reaction to drugs;
- Dust or clothes mites, books and upholstery.
The allergy may arise in an isolated situation or it can arise frequently in people who have tendencies to have allergies, and the episodes can be light or serious, and the treatment with dermatologist may be necessary.
What to do : It is necessary to move away and avoid contact with the substance that causes allergy. In some cases, it may be necessary to use anti-allergic drugs, such as Dexchlorpheniramine, Loratadine, Hydroxizine or corticosteroid ointments, for example. Learn more about identifying and treating skin allergy.
2. Skin dryness

The dry skin, a condition known as cutaneous xerosis, is caused mainly by excessive use of soaps or by very hot and time consuming baths, which causes constant itching due to irritation and peeling of the skin.
Other causes of this dry skin may include use of certain medicines, such as cholesterol-lowering drugs, opioids or diuretics, for example, in addition to situations such as dehydration, living in cold regions with low humidity, and even certain diseases that can cause changes in skin keratinization.
What to do : The treatment involves the use of moisturizing creams that contain ceramides, glycolic acid, vitamin E or urea, for example. To relieve the symptoms more immediately, it may also be necessary to use anti-allergy medicines, such as Loratadine or Dexchlorpheniramine. Check out the recipe for a great homemade moisturizer for extra dry skin.
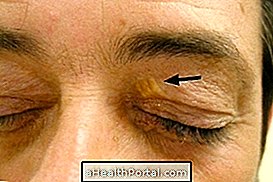
3. Dermatites

Dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disease, usually of genetic or autoimmune cause, in which there is a chronic allergic process, which causes constant and intense itching, and may be accompanied by other skin changes.
Some of the most common forms of dermatitis include:
- Atopic dermatitis : most common in folds, accompanied by redness, peeling or swelling of the skin;
- Seborrheic dermatitis : causes redness or scaling of the skin, especially on the scalp, where it may be known as dandruff;
- Contact dermatitis : causes intense itching accompanied by blisters and redness in skin sites that have been in direct contact with an irritant, such as jewelry or cosmetics, for example;
- Dermatitis herpetiformis : causes inflammatory reaction that forms small blisters on the skin that itch, similar to the herpes lesions, being more common in people with celiac disease;
- Psoriasis : is a chronic skin disease that causes inflammation and hyperproliferation of the cells of its most superficial layer, causing desquamative lesions.
More rare examples of itchy skin changes include luminar dermatitis or bullous dermatitis, as well as other dermatological diseases such as bullous pemphigoid, mycosis fungoides and lichen planus, for example. Check out more details on the major types of dermatitis.
What to do : the person with a dermatitis should be followed up by the dermatologist, who will evaluate the characteristics of the lesions and guide treatments according to each case, which may include moisturizing creams based on urea, corticoids or antiallergics, for example .
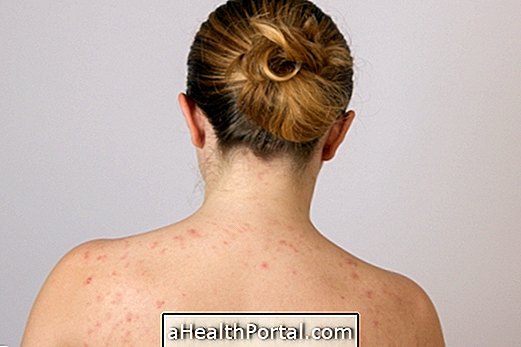
4. Skin infections

Infectious diseases that reach the skin, caused by fungi, bacteria or parasites, often cause lesions and inflammatory reactions, which causes itching. Some of the most common infections are:
- Skin Mycoses : characterized by the presence of rounded, reddish or whitish skin lesions caused by some types of fungus, and some examples are Tinea, Onychomycosis, Intertrigo and Pityriasis Versicolor;
- Cutaneous Candidiasis : Candida infection causes reddish and moist lesions, most common in the folds of the body, such as under the breasts, groin, armpits, nails or between the fingers, although it may appear anywhere on the body;
- Scabies : Also known as scabies, this disease is caused by the sarcoptes scabiei mite, which causes an intense itching and reddish lumps, and is quite contagious;
- Herpes : Herpes virus infection causes redness and small blisters, which can cause itching or be painful, being common on the lips and genital area;
- Impetigo : infection in the skin caused by bacteria that cause small wounds that contain pus and form crusts.
These infections can be transmitted from one person to another, and usually arise in situations of hygiene or impaired immunity.
What to do : The treatment is doctor-directed, made with medicines, usually ointments, to eliminate the causative microorganism, with antifungals such as Nystatin or Ketoconazole, antibiotics such as Neomycin or Gentamicin, Permethrin or Ivermectin solutions for scabies, and antiviral drugs such as acyclovir for herpes. The itching can also be alleviated with anti-allergy.
5. Systemic diseases

There are several diseases that reach the bloodstream and may present, as one of the symptoms, itchy skin. Some illnesses that can do this are:
- Viral infections such as Dengue, Zika, or Chickenpox cause changes in circulation and immunity, causing itching;
- Bile duct diseases, caused by diseases such as Hepatitis B and C, primary biliary cirrhosis, biliary carcinoma, alcoholic cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis, for example;
- Chronic renal insufficiency ;
- Neuropathies, caused by diabetes, stroke or multiple sclerosis, for example;
- Endocrinological diseases, such as hyperthyroidism, diabetes or mastocytosis;
- HIV, both due to infections of the skin, and by immune changes that may arise;
- Hematologic diseases, such as anemia, polycythemia vera or lymphoma;
- Cancer .
These diseases can cause itching with different frequency and intensity in each person.
What to do : In these cases, the doctor will indicate the treatment of the main disease, which may be causing the itching. Meanwhile, to control the symptoms, can be guided the use of anti-allergic drugs like Hidroxizine, to relieve discomfort.
6. Psychological illnesses

Psychological itching, also called psychogenic pruritus, is suspected when the cause of the itching can not be found even after detailed and lengthy medical examination with physical examinations and assessments.
This type of itching can occur in people who have diseases such as depression, bipolar disorder, anxiety, obsessive-compulsive disorder, eating disorders, drug addiction or personality disorders, for example. Sometimes the symptom is so intense that the person can live with skin lesions caused by itching.
What to do : After confirmation that it is not a dermatological or systemic disease, follow-up as a psychiatrist may be necessary, which may indicate psychotherapy or treat the underlying disease, for example with the use of anxiolytics or antidepressants.
What causes itching in pregnancy
During pregnancy, the pregnant woman undergoes changes in her body and naturally gets her skin drier, which can lead to itching.
In addition, there are some skin problems that may arise or worsen in this period, such as gestational itching, caused by alteration of the bile ducts, or other dermatoses such as urticaria, papular or gestational pemphigoid dermatosis, for example.
Thus, if the itching is persistent, and does not alleviate with hydration or withdrawal of possible allergic conditions, such as new cosmetics or cleaning products, it is recommended to consult with the obstetrician or dermatologist, to evaluate the possible causes and indicate the treatment.