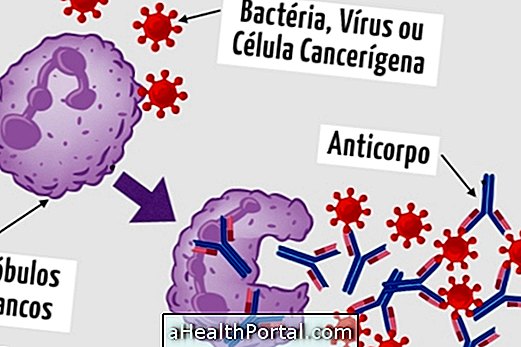
Lipoma is a type of lump that appears on the skin, which is composed of fat cells having the rounded shape, which can arise anywhere in the body and grows slowly, causing aesthetic or physical discomfort. However, this disease is not malignant and has no relation to cancer, although in very rare cases it can become a liposarcoma.
What differentiates lipoma from a sebaceous cyst is its constitution. Lipoma is composed of adipose cells and the sebaceous cyst is composed of a substance called sebum. The two diseases have similar symptoms and the treatment is always the same, surgery for removal of the fibrous capsule.
Although it is easier to have only one lipoma, it is possible that the individual has several cysts and in this case it will be called lipomatosis, which is a familial disease. Learn all about lipomatosis here.

Symptoms of lipoma
Lipoma has the following characteristics:
- A rounded lesion that appears on the skin, which does not hurt and has a firm, elastic or soft consistency, which can vary from a half centimeter to more than 10 centimeters in diameter, which already characterizes a giant lipoma.
Most lipomas are up to 3 cm in size and do not hurt but sometimes it can cause pain or a nuisance if the person gets into it. Another characteristic of lipomas is that they gradually grow over the years, without causing any discomfort for a long time, until when there is compression or obstruction in some neighboring tissue, it arises:
- Pain in place and
- Signs of inflammation such as redness or increased temperature.
It is possible to identify lipoma by observing its characteristics but to make sure that it is a benign tumor the doctor may request tests such as X-ray and ultrasound, but computed tomography can provide a better view of tumor size, density and shape .
Causes of lipoma onset
It is unknown what can lead to the appearance of these fat lumps in the body. Usually lipoma appears more in women who have similar cases in the family, and they are not common in children and have no direct relationship with increased fat or obesity.
The smaller, more superficial lipomas usually arise on the shoulders, back and neck. However, in some people it can develop in the deeper tissues, which can compromise arteries, nerves or lymphatic vessels, but in any case the treatment is done with its withdrawal in surgery.

How to treat Lipoma
The treatment for lipoma consists of performing a minor surgery for its removal. The surgery is simple, performed in the dermatological office, under local anesthesia, and leaves a small scar in place. Tumescent liposuction can be a solution indicated by your doctor. Aesthetic treatments such as lipocavitation can help remove this accumulation of fat, however, it does not eliminate the fibrous capsule, so it may come back.
The use of healing creams like cicatrene, cicabio or bio-oil can help to improve the cicatrization of the skin, avoiding the marks. See the best healing foods to consume after lipoma withdrawal.
Surgery is indicated when the lump is very large or it is located on the face, hands, neck or back, and it is disruptive to the person's life, either because they are unaesthetic or because they hamper their household tasks.