Epididymitis is the inflammation of the epididymis, a small duct that connects the vas deferens to the testis, and where sperm maturation and storage take place.
This inflammation usually causes symptoms such as swelling of the scrotal sac and pain, especially when walking or moving the region. Epididymitis can occur at any age, but it is most common between ages 14 and 35 due to infection by a bacterium or a sexually transmitted disease.
When it is caused by an infection, the epididymitis is usually acute and, therefore, the symptoms last between 1 to 6 weeks, improving like the treatment with antibiotics. However, when inflammation is caused by other factors, it may be more difficult to treat and last longer than 6 weeks, being considered chronic.

Main symptoms
The most common symptoms of epididymitis include:
- Constant low fever and chills;
- Severe pain in the scrotal or pelvic region;
- Feeling of pressure in the testicles;
- Swelling of the scrotal sac;
- Swollen tongue in the groin;
- Pain during close contact or when urinating;
- Presence of blood in the semen.
These symptoms can start lighter and get worse over time, to the point where it is not possible to move because of the intense pain. Whenever symptoms arise that may indicate a change in the testicles, it is important to consult the urologist to identify the correct cause and initiate the most appropriate treatment.
Who is at increased risk of having epididymitis
The risk of developing inflammation of the epididymis is greater in men with sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia and gonorrhea. However, epididymitis can also occur if there is another infection such as tuberculosis, prostatitis or urinary tract infection.
In boys, epididymitis usually arises after a strong blow in the intimate region or by torsion of the testicle. In either case, the symptoms are similar to the adult and should be treated as soon as possible in the hospital.
How to confirm the diagnosis
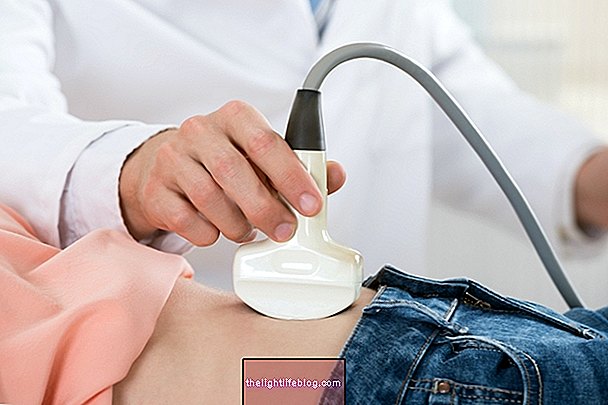
Diagnosis of epididymitis can be made by the physician only on the basis of observation and palpation of the intimal region, but may need to be confirmed by examinations such as urine examination, Doppler ultrasound, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging.
How is the treatment done?
Since most cases of epididymitis are caused by an infection, treatment is usually initiated as use of antibiotics such as:
- Doxycycline;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Ceftriaxone.
These antibiotics should be taken for up to 4 weeks, as directed by your doctor, even if the symptoms have improved.
In addition, to alleviate the symptoms it is still advised to keep the rest, avoid picking up on very heavy objects and applying ice in the area. The urologist may also prescribe anti-inflammatory and analgesic remedies such as Ibuprofen or Paracetamol, to improve well-being during recovery.
This type of treatment usually has a lot of success and the improvement of the symptoms appear in about 2 weeks, however, in some cases the epididimite can take up to 3 months to disappear completely. In these cases, the doctor may also assess the need for surgery, especially if the epididymitis is not caused by an infection but rather by a change in the anatomy of the testicles, for example.