Hypovolemic shock, also known as hemorrhagic shock, occurs when about 1 liter of blood is lost, which causes the heart to stop being able to pump the necessary blood to the whole body, leading to serious problems in various organs of the body. body and life-threatening.
Some symptoms of this type of shock include:
- Constant headache, which can get worse;
- Excessive tiredness and dizziness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Very pale and cold skin;
- Confusion;
- Bluish fingers and lips;
- Feeling of fainting.
In many cases, hypovolemic shock may be easy to identify, especially if the bleeding is visible, however, in cases of internal bleeding, these signs may be more difficult to detect.
This type of shock is usually more frequent after very strong strokes, such as traffic accidents or high altitude falls, but can also happen during surgeries, for example.
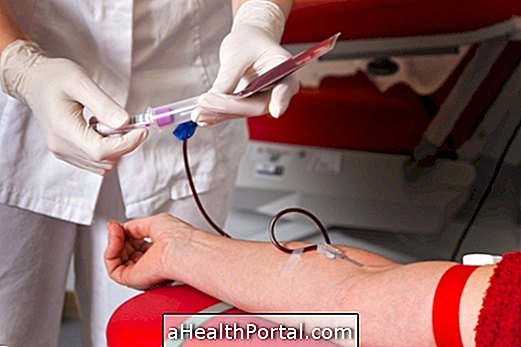
To treat this shock and avoid its serious consequences you need to go to the hospital to initiate blood transfusion or the administration of serum directly into the vein, as well as treating the cause that is causing the loss of blood.
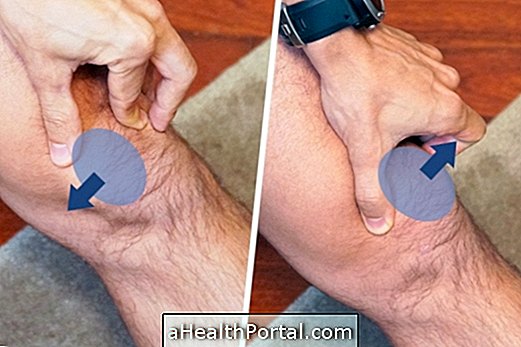
First aid for hypovolemic shock
Hypovolemic shock is an emergency situation that should be addressed as soon as possible. Thus, if there is suspicion, one should:
- Immediately call for medical help, calling 192;
- Lay the person down and raise their feet about 30 cm, or enough to be above heart level;
- Keep the person warm by using blankets or clothing;
If there is a bleeding wound, it is important to try to stop the bleeding by using a clean cloth and putting pressure on the site to minimize blood loss and allow more time for medical staff to arrive.
Possible causes
Hypovolemic shock usually arises when there is a bleeding that causes excessive blood loss, as in cases of:
- Very deep wounds or cuts;
- Traffic-accidents;
- Falls of great height;
- Internal bleeding;
- Ulcers active, bleeding;
- Menstruation very intense.
In addition, other situations that cause the loss of body fluids may also contribute to the decrease in the amount of blood in the body. Some of these causes include prolonged diarrhea, very severe burns or excessive vomiting, for example.
How is the treatment done?
The treatment for hypovolemic shock is done through blood transfusion and the administration of serum directly into the vein, and it is essential to stop the cause of the bleeding, or the situation that leads to the loss of fluids.
Death caused by hypovolemic shock only occurs if the amount of blood and fluid lost corresponds to more than 1/5 of the total volume of blood of a human being, which means approximately 1 liter of blood.